3D Printing PLA - All You Need To Know
 Image Courtesy - Marco Verch via Flickr
Image Courtesy - Marco Verch via Flickr
PLA, or polylactic acid, is a popular and commonly used 3D printing polymer. It's likely to be among the first materials you try with your 3D printers. It is easy to print, cheap, and comes in many different types for many different uses.
There are still a lot of questions about PLA material on various community forums. How do you print it? What is the best printing temperature? Slicing options? These are just a handful of the many queries that consumers have about the PLA filament.
This article aims to answer these questions for good. We'll delve deep into the world of PLA filament in this post and learn everything there is to know about it. By the end, you'll have answers to all of your PLA questions and feel confident in printing it.
Continue reading to improve your PLA skills and 3D print some high-quality models. Let's get started!
What is PLA filament?

Image Courtesy - Alvin Trusty via Flickr
As a biodegradable 3D printing material, PolyLactic Acid (PLA) is commonly derived from maize starch and sugar cane. It prints easily, has an excellent surface polish and is one of the cheapest 3D printing filaments on the market today.
As for its physical properties, PLA is a hard plastic. PLA-printed parts have a lower tensile strength than ABS or PETG prints. While it is not the most durable material, it is perfect for printing aesthetic and show items.
PLA is also one of the most common materials used for 3D printing right now. Many people who use 3D printers prefer PLA because of its low cost, wide selection, and simple printability.
Now that we have a basic grasp of the material let's look at some of its advantages and everything you need to know about 3D printing with PLA.
Why 3D Print with PLA?
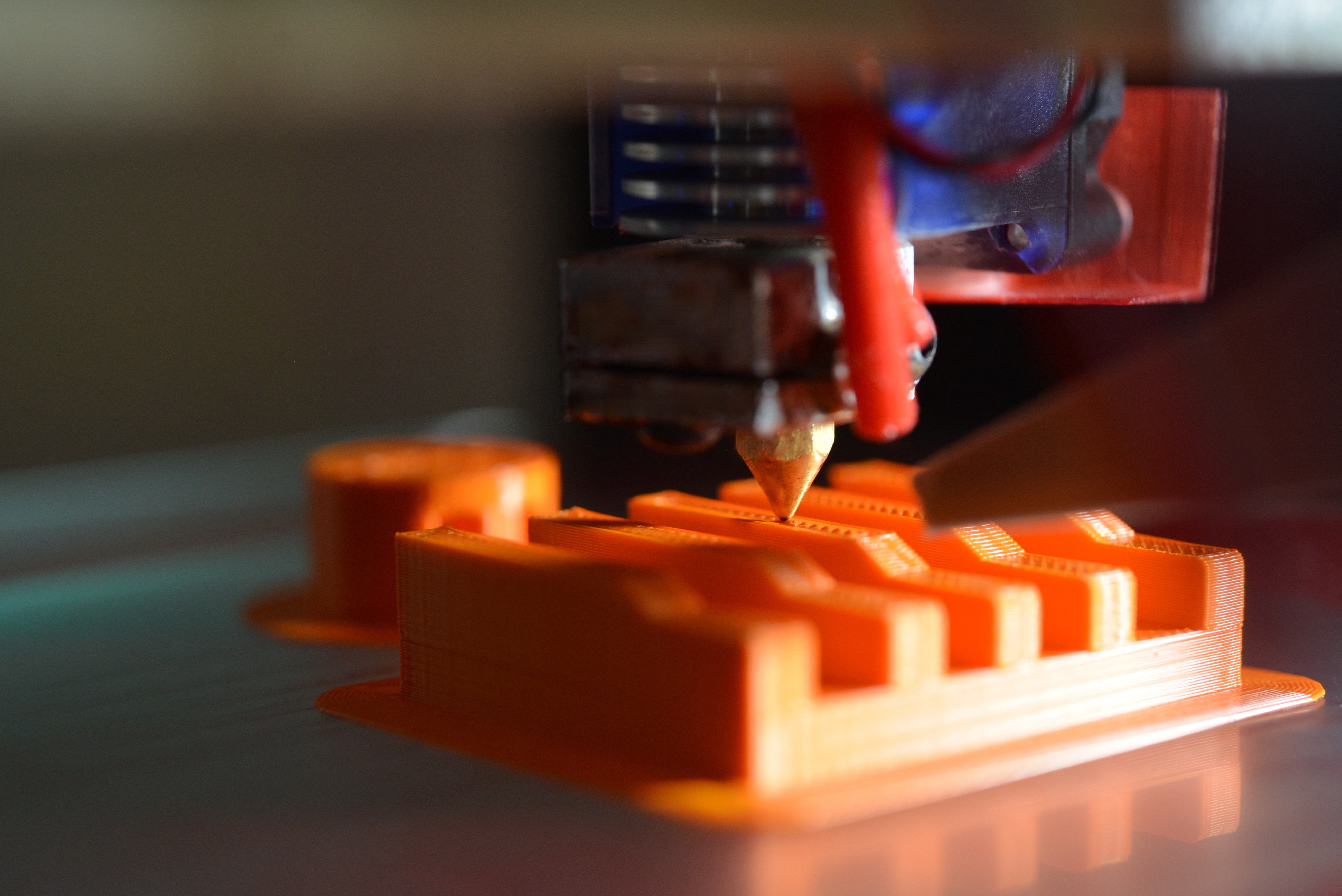 Image Courtesy - Photo by Kadir Celep on Unsplash
Image Courtesy - Photo by Kadir Celep on Unsplash
PLA is the best material to start with. Everyone who has ever tried their hand at 3D printing probably did it with PLA. There are a number of reasons why PLA is so popular as a 3D printing material. This section will examine a couple of these advantages.
Low Printing Temperature
The optimal temperature range for printing with PLA is between 190 and 210 °C. You can print it on almost any 3D printer at this temperature. There's no reason for your printer to have a high-temperature hot end. Energy expenditures are reduced to a lesser extent by the low temperature as well.
Easy to 3D Print
When it comes to 3D printing, PLA is one of the most user-friendly materials. You can get by without a heated print bed, an enclosure, or any other high-end accessories. PLA is less prone to warping, and with adequate bed adhesion, prints will not fall off the bed during printing.
The slicing settings for PLA are also pretty easy to understand. The printer needs very little tweaking to produce high-quality prints.
Widely accessible
As a result of its widespread popularity as a 3D printing material, PLA can be found in almost every country. Several different types and colors of PLA are available. Virtually every 3D printer manufacturer delivers a roll of PLA with their machine for the first testing.
PLA is a great material for people in all kinds of fields because it is easy to get to and gives you a lot of options.
Biodegradable
PLA stands out as one of the few sustainable options. It’s biodegradable, meaning it’ll disintegrate biologically and not add to plastic pollution.
Nonetheless, this quality should be taken with a grain of salt. While PLA is biodegradable, the process might be lengthy. For the really ecologically conscientious users, it’s advisable to recycle PLA rather than just discard your prints elsewhere.
Extensive Support
Because PLA is well-known and easy to find, it's easy to get help for it in any way you can think of. Any question you've ever had regarding PLA has probably already been answered. There is a wealth of resources available online for learning about and fixing issues with PLA.
This makes it easy for newcomers to start using PLA and learn more about 3D printing in general.
Why not 3D Print with PLA?
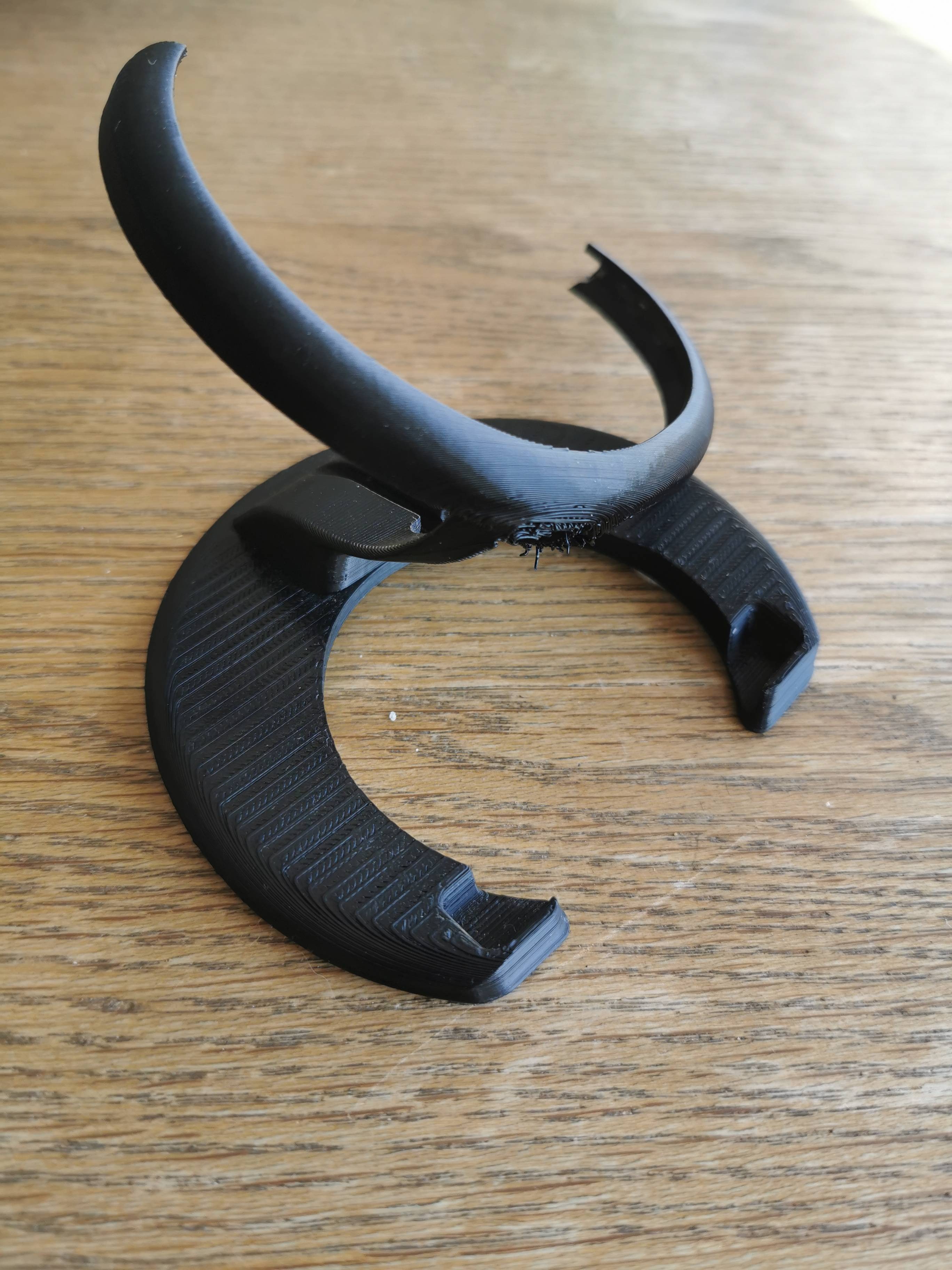

Image Courtesy - OverenthusiasticWind via Reddit
Low Heat Resistance
At 180 °C is when PLA begins to melt and flow, while between 50 and 80 °C is when it begins to distort. This temperature is fairly low and not good for most functional prints. You also can’t expose your PLA prints to the sun, or else they’ll begin to lose their shape.
PLA deforms readily in comparison to other filaments such as ABS and PETG and is only ideal for attractive indoor printing.
Poor tensile properties
PLA is a brittle thermoplastic by nature. PLA-printed components have a high degree of hardness and brittleness. So, it's not a material that can stretch or bend. It's especially important for prints that will be under continual stress.
PLA parts won't break slowly; instead, they'll just snap. Because of this and the fact that PLA has a low glass transition temperature, it can't be used to make functional or load-bearing parts.
Extremely Hygroscopic
In humid environments, PLA has a higher tendency to take in water from the atmosphere. As a result, you'll have a poor printing experience and prints that break easily. Because of its sensitivity to moisture, PLA printing and storage necessitate equipment such as a dry box.
Challenging to Post-Process
Due to PLA's characteristics, finishing your pieces might be difficult. As a result of its toughness, sanding and polishing a PLA print is a time-consuming process. However, unlike with ABS prints, which can be easily refined with acetone, PLA prints have no such easy options. That increases the work and time required for PLA components, which raises your overall expenses.
Slicer settings for PLA
 As opposed to other printing materials, PLA is quite simple to work with. Using PLA for 3D printing requires just attention to a few simple settings. Let's take a look at some of PLA's most relevant settings.
As opposed to other printing materials, PLA is quite simple to work with. Using PLA for 3D printing requires just attention to a few simple settings. Let's take a look at some of PLA's most relevant settings.
Print Temperature
PLA printing temperatures average between 190 and 210 °C. Each filament roll has a unique optimal printing temperature. The best way to figure out the print temperature for your PLA filament roll is to use a temperature tower. It will help you figure out at what temperature you should print to get the best results.
Bed Temperature
The use of a heated bed is not strictly necessary when 3D printing with PLA. It is less prone to warping and problems with bed adhesion.
But, if you have a heated print bed, it's always best to use it for PLA parts. PLA material performs best at a bed temperature of 50-60 °C. In the case of big prints, it aids in reducing the lifting of corners.
Bed Surface
Printing on glass, BuildTak sheets, PC sheets, or PEI is quite successful. With a glass print bed, you can use painter's tape to make it stick better. Prints stick well on it and peel off easily thereafter.
Even so, PEI print bed and BuildTak, two examples of flexible bed surfaces, offer the best performance and user ease. PLA pieces stick without glue and peel off with a little wiggle once printing is complete.
Print Speed
On a printer that has been fine-tuned, a print speed of 40–80 mm/s is a good range for printing with PLA. These speeds let the PLA material cool down slowly and cut down on any extra oozing.
For optimum results when printing PLA on a standard Ender 3 printer, set the print speed to between 40 and 60 mm/s. If you go any higher, you run the danger of under-extrusion, ringing, and poor print quality.
Printers utilizing the Klipper firmware, such the Voron, have no trouble printing at rates of above 200 mm/s with PLA. The top speed of the newest Bambulab printer is estimated to be about 500 mm/s. These machines are designed primarily for producing models at fast rates while maintaining print quality.
Cooling
While printing with PLA, you must have the component cooling fan running continuously. The freshly extruded layer needs to be cooled down as quickly as possible to reduce the chances of oozing or warping.
During the first two layers, reduce the fan speed to half. This will help the first layers stick to the bed better. After that, you can set the part cooling fan speed to 100% for the rest of the print.
Retraction settings
While fine-tuning the retraction parameters, speed and distance are the two most important variables to keep in mind.
Best results are achieved with a retraction speed of 50–60 mm/s and a retraction distance of 0.5–1 mm on direct drive extruders. For Bowden extruders, the speeds range from 40 to 60 mm/s, and the distance is between 2 and 7 mm.
The precise figures depend on your printer, filament spool, and a variety of other things. The easiest approach to determine the optimal retraction settings for your PLA filament is to do a Retraction tuning test.
Post-Processing PLA parts
Sanding and Painting
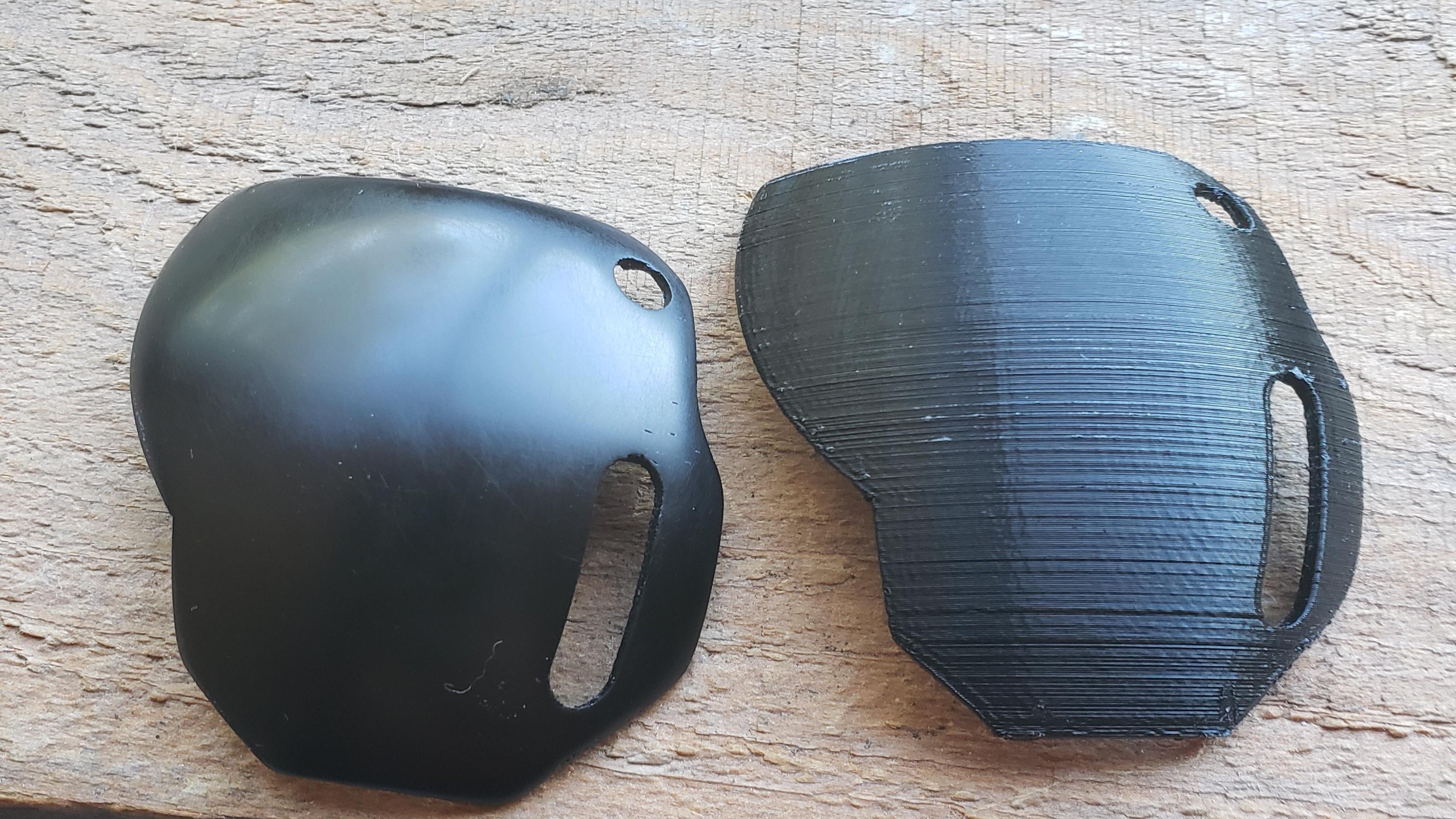

Image Courtesy - AxeCatAwesome via Reddit
One of the most frequent and straightforward methods of post-processing your PLA prints is by sanding them. If there are any obvious layer lines, you may sand them down with normal sandpaper to get a smooth surface. We recommend beginning with 200 grit sandpaper and working your way up to a finer grain ~4000 grit.
Wet polishing also works great on PLA parts. With a little water and fine-grit paper, you can give your prints a smooth finish.
When it comes to painting, PLA is easy to work with and paint. Priming the surface first will even it out and hide any imperfections. And a final coat of paint can make your parts look better.
PLA Smoothing
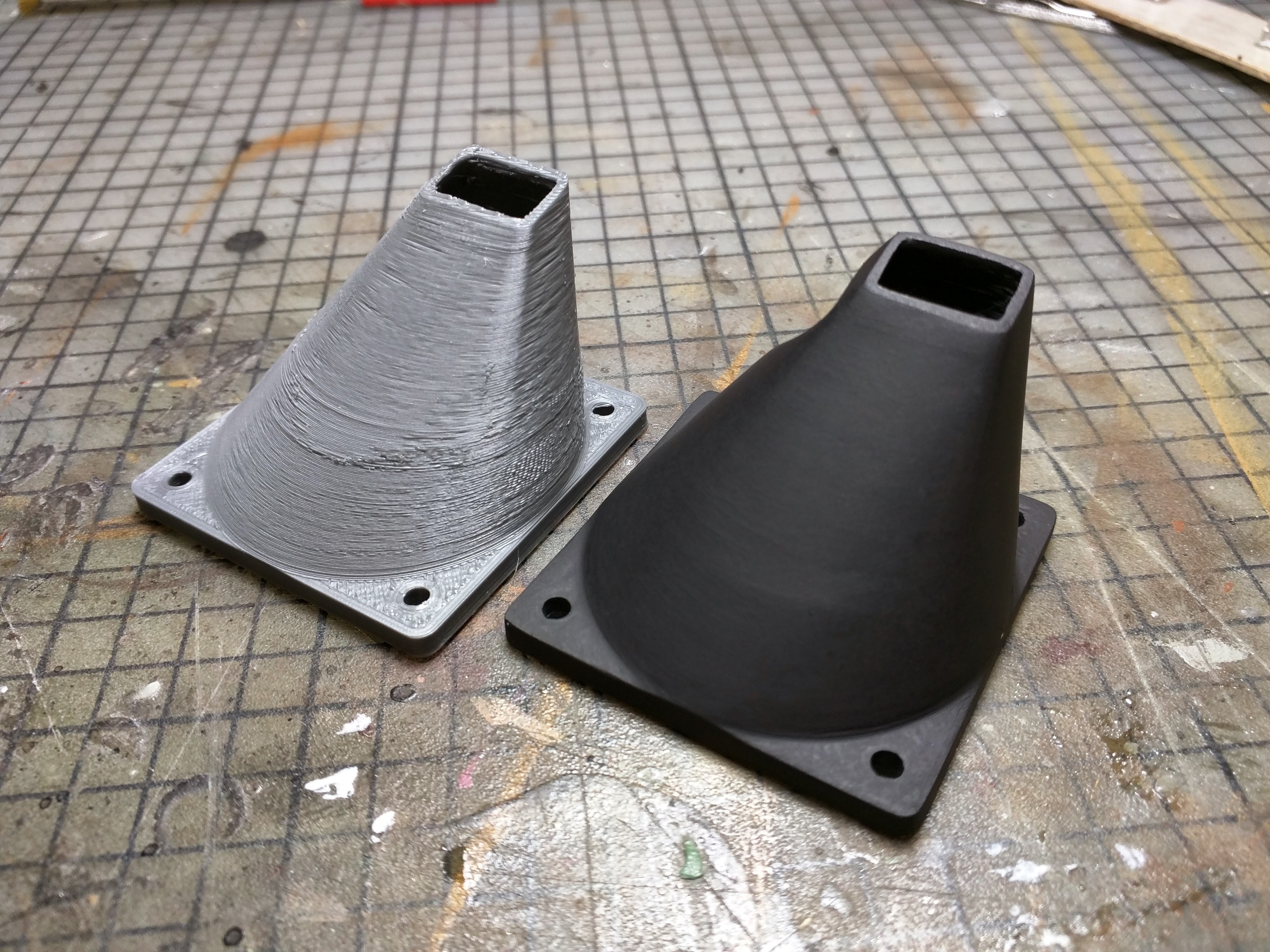 Image Courtesy - amwatts via Reddit
Image Courtesy - amwatts via Reddit
Sanding is a manual operation that involves a lot of work and time. It's not always the best option for every component. An alternative to that is chemically smoothing PLA parts.
XTC3D
XTC3D is a coating made of epoxy and resin that is made to cover and smooth out plastic parts. It dries at a lower temperature than conventional two-part epoxy resins, so PLA prints won't melt.
Once mixed, you just need to put a coating of XTC3D over your PLA parts. After the resin cures, it will leave behind a strong, glossy surface that is perfect for printing. It's the cleanest and simplest method for removing imperfections from PLA prints.
But it makes your parts less detailed and isn't good for smaller prints like miniatures. It works well with large prints that don't require a lot of fine detail.
3D Gloop
The primary function of 3D Gloop is as an adhesive for PLA and ABS. But, it is also effective for enhancing the finish of your PLA prints.
It consists mostly of Methylene Chloride and Methyl Acetate, among other compounds. It works by melting the PLA layers just a little bit and joining two parts together. It seems this method is effective for finishing the surface of the parts as well.
All you have to do is gently brush a layer of 3D Gloop on your prints and let it dry for a while. It will smooth up your prints by fusing the layer lines together.
Polymaker PolySmooth™
PolySmooth™ filament isn't a perfect match for PLA, but it shares many of the same properties. PolySmooth™ filament is a PolyVinyl Butyral (PVB)-based material that behaves similarly to PLA while 3D printing.
The advantage though is that you can smoothen up this filament similar to ABS material. It responds to alcohol and melts when exposed to it. The Polysher by Polymaker is made for post-processing materials like the PolySmooth™ filament.
It gives your parts an Isopropyl alcohol bath and melts away the upper surface. This results in a smooth surface with practically no apparent layer lines and the items come out appearing as though injection molded.
It’s a good solution if you want the benefits of ABS smoothness for your components, but with the easy printability of PLA material.
Furthermore, ethyl acetate, pyridine, tetrahydrofuran, and dichloromethane have all been shown to melt and smooth PLA. But they are very dangerous, hard to get, and often require a lot of safety precautions to use. It's better to avoid these chemicals and stick to the above options, which are safer.
Tips and Tricks for 3D Printing PLA
Image Courtesy - Photo by Kadir Celep on Unsplash
Dry your Filament
Being hygroscopic in nature, PLA readily absorbs moisture from the air. This causes under-extrusion, brittle prints, and bubbles on the print surface.
It's always best to keep your PLA dry when you store it and use it. In order to preserve your PLA material, you should use a dry box, food dehydrator, or specialized filament dehydrator. Machines like this will keep your filament from becoming wet, allowing you to print with more consistency.
Fine tune print settings
It's important to take your time while configuring your slicer for PLA. The most significant effects on print quality come from playing with the print temperature, cooling, and retraction parameters.
To fine-tune your slicer settings and enhance your print quality, use calibration prints like Temperature towers and Retraction tests. SuperSlicer's calibration menu is where you'll find all the available calibration models. You can easily fine-tune your PLA prints by using it.
Use a Heated Bed
Although it is possible to print PLA without a heated bed, the print quality is likely to increase if you use one. You'll see less corner lifting and warping in your prints, and the bed adhesion will increase significantly.
Use high-quality PLA
If you want better printing results and an overall better printing experience, choose a high-quality PLA. Low-priced PLA materials usually suffer from subpar quality control. Low-quality PLA filaments have a number of issues, including tangled filament, a filament diameter that varies widely, and several additives and contaminants.
While utilizing PLA, stick with reputable brands only. Check out the reviews, look at the technical specs, and see if the manufacturer is known to have any problems. Better to pay a little more now to avoid problems and bad printing quality later.
Final Thoughts
PLA is a gem of a material. It's one of the most user-friendly 3D printing materials due to its low pricing, high adaptability, and simple printing process.
PLA filament has a lot of benefits, such as a low printing temperature, biodegradability, and no need for a heated print bed. Yet, its weakness lies in its poor heat resistance and tensile properties.
But there's no need to worry. With the right slicer settings and printing techniques you can make 3D printing with PLA an enjoyable and rewarding experience. So go ahead and explore the world of PLA printing and let your creativity soar!
