Тест на втягивание в OrcaSlicer: подробное руководство.
Введение
3D-печать — это захватывающая технология, позволяющая создавать практически всё, что только можно себе представить. Однако она также сопряжена с некоторыми проблемами и ограничениями, такими как качество напечатанных деталей. Одна из наиболее распространенных проблем, влияющих на внешний вид и функциональность 3D-отпечатков, — это наличие нежелательных остатков материала, таких как нити, капли и сгустки.
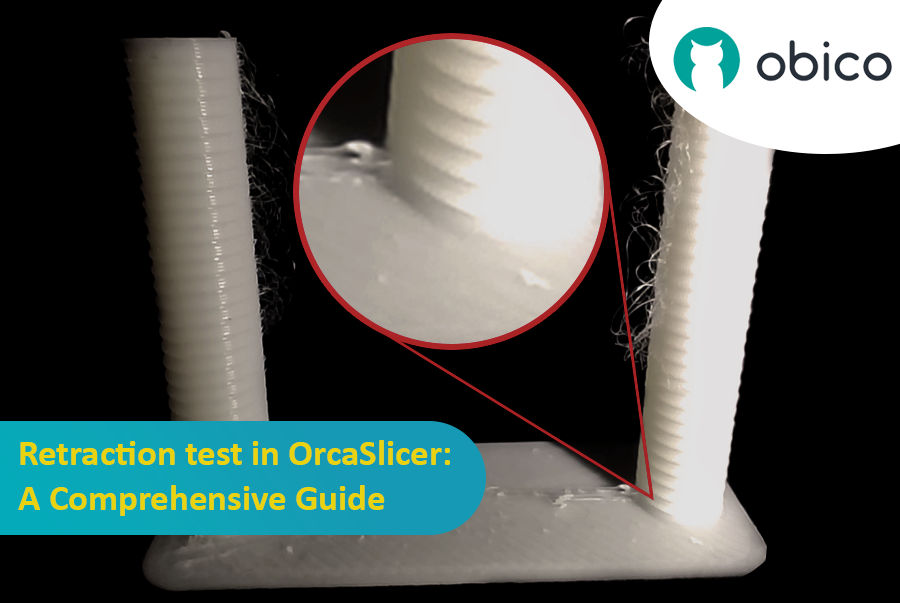
К счастью, существует способ уменьшить или устранить эти артефакты с помощью функции, называемой ретракцией. Но что означает ретракция?
Давайте разберем это по пунктам:
Что такое ретракция и тест на ретракцию?
Тест на втягивание — это процедура калибровки, направленная на уменьшение или устранение проблем с образованием нитей и подтеканием, которые могут возникнуть во время 3D-печати. Образование нитей и подтекание вызваны избытком материала, вытекающим из сопла, когда нагревательный элемент перемещается от одной части модели к другой без экструзии. Это приводит к образованию нежелательных нитей или сгустков филамента на поверхности или между частями модели, что влияет на качество и внешний вид печати.
Чтобы предотвратить это, функция ретр�акции в программном обеспечении для нарезки моделей дает указание экструдеру оттянуть или втянуть определенное количество нити перед выполнением перемещения. Это создает отрицательное давление внутри сопла, уменьшая поток расплавленного пластика. Расстояние ретракции и скорость — это два основных параметра, которые контролируют, насколько и как быстро втягивается нить. Однако найти оптимальные значения этих параметров может быть сложно, поскольку они зависят от различных факторов, таких как тип нити, размер сопла, тип экструдера, скорость печати и температура.
Тест на втягивание нити — это метод систематического тестирования различных комбинаций расстояния и скорости втягивания нити и наблюдения за их влиянием на качество печати. Распечатав серию тестовых моделей с различными настройками втягивания, мы можем сравнить результаты и выбрать оптимальные значения для нашей конкретной конфигурации и филамента. Тест на втягивание нити помогает добиться более чистой и плавной печати без увеличения времени печати или расхода материала.
В этой статье мы шаг за шагом р�асскажем, как выполнить тест на втягивание нити с помощью OrcaSlicer, мощного и удобного программного обеспечения для нарезки моделей, поддерживающего различные 3D-принтеры и филаменты. Мы объясним, как использовать встроенную функцию теста на втягивание нити в OrcaSlicer, а также как вручную настроить параметры втягивания в профилях принтера и филамента. Следуя этому руководству, вы сможете улучшить свой опыт 3D-печати и насладиться преимуществами втягивания нити.
Прежде чем подробно рассказывать о том, как выполнить тест на втягивание, давайте начнем с краткого обзора OrcaSlicer и объясним, почему стоит использовать встроенный в него тест на втягивание.
Что такое OrcaSlicer?
OrcaSlicer — это программа для нарезки моделей с открытым исходным кодом для FDM-принтеров. Она является форком Bambu Studio, популярного программного обеспечения для нарезки моделей для 3D-принтеров BambuLab. OrcaSlicer был разработан программистом, который хоте�л улучшить оригинальное программное обеспечение и добавить больше функций и опций для пользователей. Основные особенности OrcaSlicer:
- Автоматическая калибровка для всех принтеров
- Режим «Сэндвич» (внутренний-внешний-внутренний) — улучшенная версия режима «Внешние периметры»
- Точная толщина стенок
- Поддержка преобразования полиотверстий
- Поддержка Klipper
- Более детальное управление
OrcaSlicer доступен для платформ Windows, Mac и Linux. Вы можете скачать последнюю стабильную или ночную версию по ссылке Страница на GitHub.
Если вас заинтересовала программа OrcaSlicer и вы хотите узнать о ней больше, ознакомьтесь с нашей ссылкой подробное руководство. Там рассматриваются основы и приводятся ссылки на более подробные разделы, которые помогут вам расширить свои навыки.
Почему это полезно для проверки на втягивание?
OrcaSlicer полезен для тестирования ретракции, поскольку позволяет легко регулировать параметры скорости и расстояния ретракции в слайсере. Вы также можете использовать встроенный тест калибровки ретракции для генерации пользовательского G-кода для тестирования различных настроек ретракции. OrcaSlicer также поддерживает режим «сэндвич», в котором внутренний и внешний периметры печатаются отдельно, что уменьшает необходимость ретракции и улучшает качество поверхности.
Кроме того, программа предлагает различные варианты настроек ретракции, позволяющие адаптировать параметры под разные материалы и модели принтеров для достижения наилучших результатов.
Теперь, когда вы поняли, что такое тест на втягивание нити и почему OrcaSlicer полезен для оптимизации настроек втягивания, давайте перейдем к практике. Мы рассмотрим шаги по запуску теста на втягивание нити на вашем 3D-принтере.
Шаг 1: С�качайте и установите OrcaSlicer
Вы можете скачать OrcaSlicer с его страницы на GitHub: OrcaSlicer GitHub. Следуйте инструкциям по установке на ваш компьютер.
Шаг 2: Выберите принтер, филамент и технологию печати
Откройте OrcaSlicer и выберите принтер, филамент и процесс, которые вы хотите использовать для теста. Вы можете использовать профили по умолчанию, которые поставляются с программой, или создать свои собственные пользовательские профили, если у вас есть другие настройки.
Шаг 3: Активируйте функцию проверки втягивани�я
После создания нового проекта перейдите в меню Калибровка OrcaSlicer и выберите пункт «Тест ретракции». Откроется новое окно, где вы сможете настроить параметры башни ретракции. Башня ретракции — это 3D-модель, состоящая из различных секций с разной длиной ретракции. Распечатав её, вы сможете увидеть, как каждая длина ретракции влияет на качество печати.
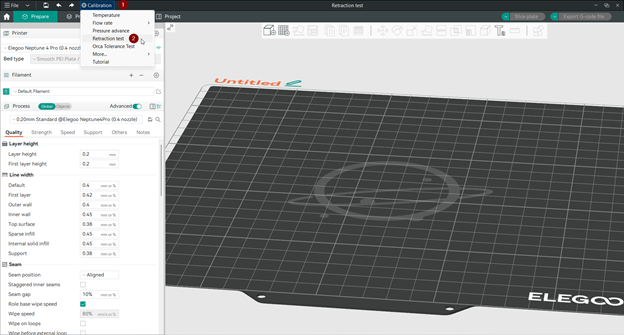
Настройки втягивающей башни следующие:
-
Начальная длина втягивания: Это длина втягивания для первого участка башни. Значение по умолчанию — 0 мм, что означает отсутствие втягивания.
-
Конечная длина втягивания: Это длина втягивания для последнего участка башни. Значение по умолчанию — 2 мм, что означает втягивание на 2 м�м.
-
Шаг: Это величина увеличения длины втягивания для каждого участка башни. Значение по умолчанию — 0,1 мм, что означает, что длина втягивания увеличивается на 0,1 мм для каждого участка, пока не достигнет конечного значения. Меньший шаг обеспечивает более точный тест, но также увеличивает длину башни.
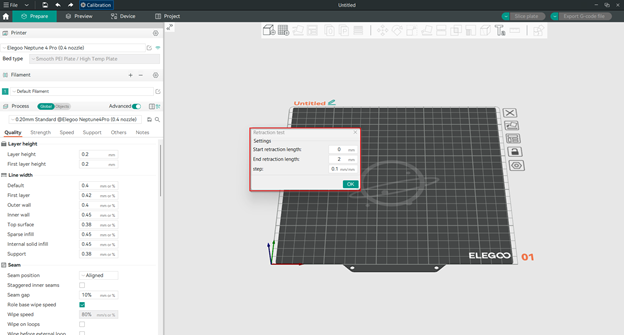
Шаг 4: Настройка длины втягивания
Ключ к успешному тестированию ретракции — выбор правильного диапазона длин ретракции. OrcaSlicer позволяет вводить эти значения, поэтому вы можете использовать настройки по умолчанию или изменить их в соответствии со своими потребностями. Цель состоит в том, чтобы протестировать различные длины ретракции и найти ту, которая максимально уменьшает образование нитей и подтекание без ущерба для качества печати.
Рекомендуемая длина втягивания нити может зависеть от типа используемого экструдера:
-
Для экструдеров с прямым приводом, у которых расстояние между экструдером и соплом невелико, настроек по умолчанию обычно достаточно. Можно начать с 0 мм и закончить на 2 мм с шагом 0,1 мм.
-
Для экструдеров Боудена, у которых между экструдером и соплом находится длинная трубка, может потребоваться большая длина втягивания. Можно начать с 1 мм и закончить на 6 мм с шагом 0,2 мм.
Шаг 5: Нарежьте и распечатайте башню для втягивания нити
После настройки параметров башни ретракции появится новый проект с башней ретракции. Вы можете нарезать проект и распечатать его. Башня имеет несколько выемок, каждая из которых соответствует разной длине ретракции. Посмотрев на башню после печати, вы сможете увидеть, как каждая длина ретракции влияет на качество печати.
Отдохните с Obico
Совет: Изучите Обико для ОктоПринт и Клиппер!

Пока ваш ретракционный узел печатает, почему бы не познакомиться с Obico, лучшим программным обеспечением для интеллектуальной 3D-печати? С Obico вы можете отслеживать и контролировать свой 3D-принтер с любого устройства и из любого места. Вы также можете расслабиться благодаря системе обнаружения сбоев на основе искусственного интеллекта Obico, которая следит за процессом печати и уведомляет вас о любых проблемах. Подключите свой принтер к Obico бесплатно и наслаждайтесь неограниченной трансляцией с веб-камеры, уведомлениями о состоянии 3D-принтера, удаленным доступом к 3D-принтеру и многим другим!

Obico также предлагает мобильные приложения для iOS и Android, позволяющие получать доступ к 3D-принтеру и управлять им с любого устройства и в любом месте. Присоединяйтесь к Obico бесплатно и наслаждайтесь непревзойденным опытом 3D-печати.
Шаг 6: Анализ результатов
Оптимальная длина ретракции — самая короткая, которая минимизирует образование нитей и подтекание без ухудшения качества печати. Проверьте каждую выемку на шаблоне и найдите ту, которая обесп�ечивает наиболее чистый результат. Это оптимальная длина ретракции для вашего принтера и филамента.
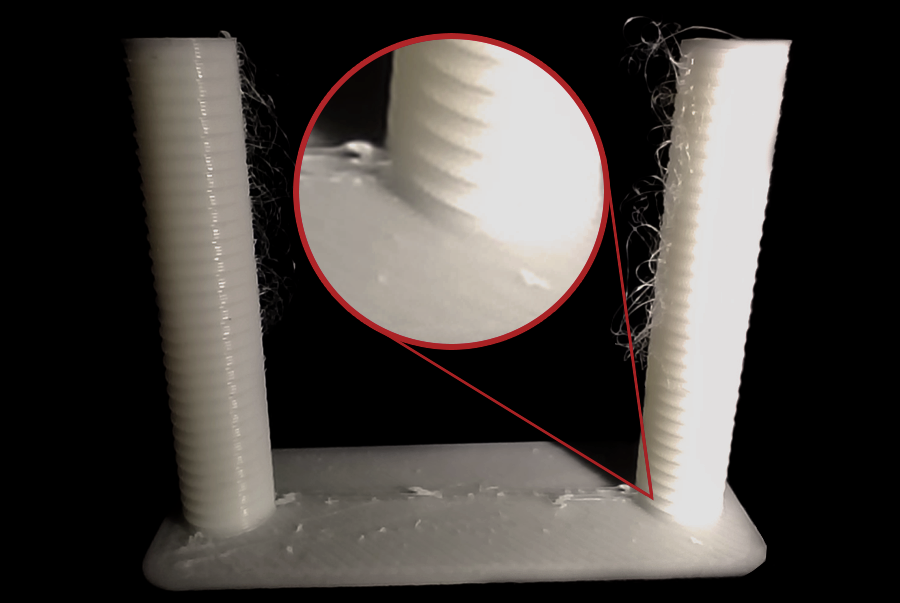
Как видно из нашего теста, образование нитей наблюдается в верхней части башни для втягивания нити, а наилучшее качество достигается на расстоянии одной выемки от основания башни, и поскольку шаг составляет 0,1 мм, то оптимальное значение втягивания для этой нити составляет 0,2 мм.
Шаг 7: Настройте параметры
После того, как вы определите оптимальную длину ретракции, вы можете изменить настройки филамента в OrcaSlicer, используя это значение. Это поможет вам печатать с лучшим качеством, без образования нитей и подтекания.
Длину втягивания нити следует настраивать индивидуально для каждого типа нити, поскольку она различается. Вот пошаговая инструкция:
-
Откройте настройки филамента, щелкнув по маленькому значку настроек.
-
Перейдите во вкладку Переопределения настроек.
-
Установите флажок длина в настройках ретракции.
-
Введите новое оптимальное значение длины.
-
Затем нажмите на значок сохранения, чтобы сохранить новое значение.

Это позволит заменить настройки принтера новым, обновленным значением при следующем выборе этого филамента.
Советы по проектированию успешной выдвижной башни:
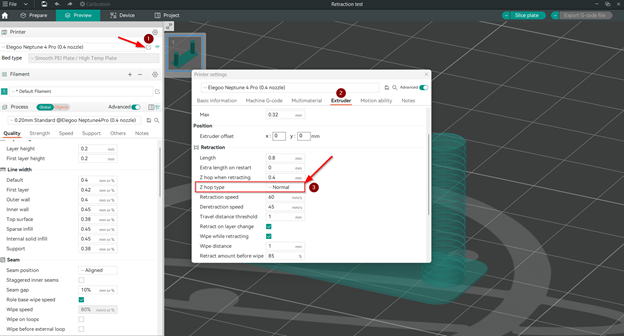
- В настройках ретракц�ии принтера обязательно выберите тип ретракции Normal, так как другие варианты могут повлиять на результаты работы ретракционной башни и привести к неточным результатам.
Для этого выполните следующие простые шаги:*
- Откройте настройки принтера.
- Нажмите на вкладку «Экструдер».
- Выберите тип Z-подскока Обычный.
Примечание: В этой статье мы более подробно рассмотрим типы Z-образных прыжков.
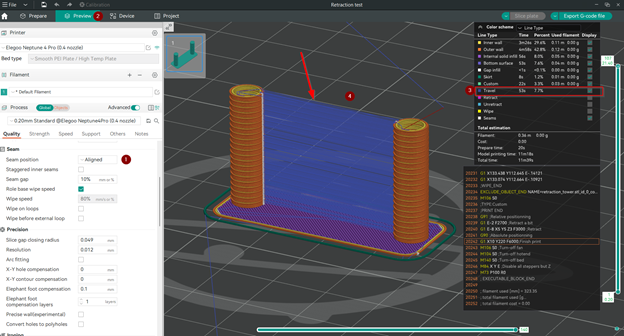
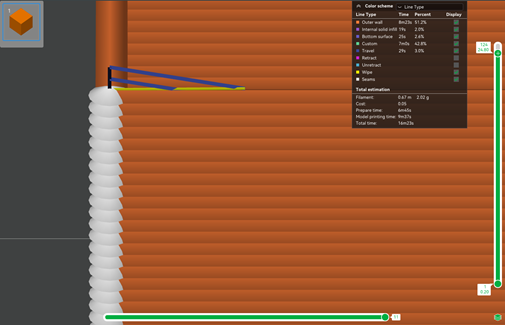
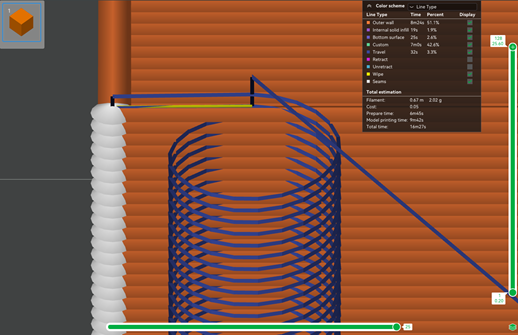
- Убедитесь, что перемещение происходит непосредственно между двумя башнями, выбрав положение Выровненный шов. Вы также можете просмотреть перемещение (отображается синим цветом), выполнив действия, показанные на изображении ниже.
Если в предварительном просмотре движение перемещения между двумя башнями не совпадает, вы можете выполнить это вручную. Вот как это сделать:
- На вкладке «Подготовка» выберите модель, а затем в плавающем горизонтальном меню выберите «Покраска швов».
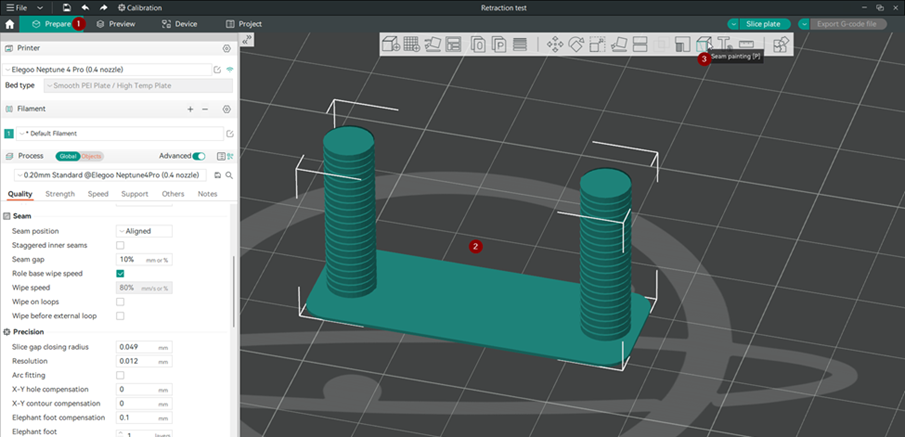 2. Нарисуйте вертикальный шов на внутренней стороне каждой башни так, чтобы они располагались друг напротив друга.
2. Нарисуйте вертикальный шов на внутренней стороне каждой башни так, чтобы они располагались друг напротив друга.
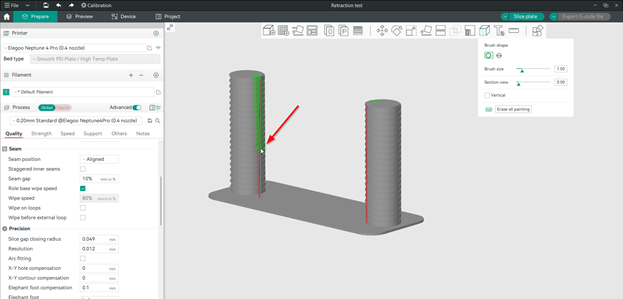 3. Нажмите на тарелку для нарезки.
3. Нажмите на тарелку для нарезки.
Теперь при предварительном просмотре вы должны увидеть движение между двумя башнями, отображаемое синим цветом.
Дополнительные соображения
К другим факторам, которые могут повлиять на результаты теста на ретракцию, относятся:
-
Тип филамента: Некоторые материалы, такие как PLA или ABS, менее склонны к вытеканию, чем другие. Для таких материалов вы можете использовать меньшую длину ретракции (0,2–0,4 мм).
-
Устранение неполадок: Если после теста на ретракцию у вас по-прежнему возникают проблемы с образованием нитей, возможно, вам потребуется просушить филамент или проверить правильность установки сопла.
Подробный анализ настроек ретракции принтера в OrcaSlicer
Давайте подробно рассмотрим настройки ретракции и параметры в OrcaSlicer для лучшего контроля над процессом печати.
Когда вы откроете настройки принтера, чтобы получить доступ к разделу ретракции, вы увидите следующие параметры:
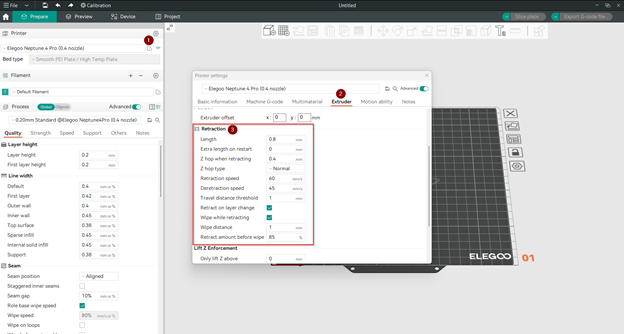
- Длина втягивания:
- Это количество нити в экструдере, которое оттягивается назад, чтобы избежать подтекания при длительной транспортировке. Установите значение 0, чтобы отключить ретракцию.
- Дополнительная длина при перезапуске:
- При компенсации ретракции после перемещения экструдер будет проталкивать это дополнительное количество нити. Эта настройка требуется редко.
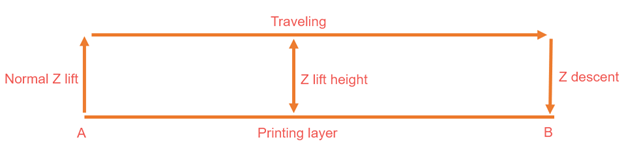
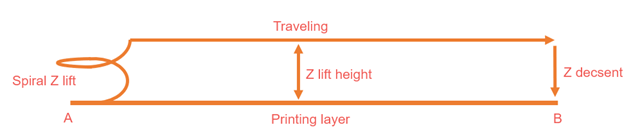
- Подпрыгивание по оси Z при ретракции:
- Когда принтер оттягивает материал, он также немного приподнимает сопло. Это гарантирует, что сопло не коснется напечатанного объекта при перемещении в другое место. Сопло не может быть поднято более чем на 5 мм.
- Тип Z-подскока:
- Мы объясним несколько вариантов Z-образного подъема сопла после завершения его втягивания.
- Наклон
- В этом режиме сопло перемещается вверх по диагонали, сокращая расстояние и время пер�емещения.
 2. Нормальный
2. Нормальный
- В этом режиме сопло движется вверх и вниз по прямой линии.
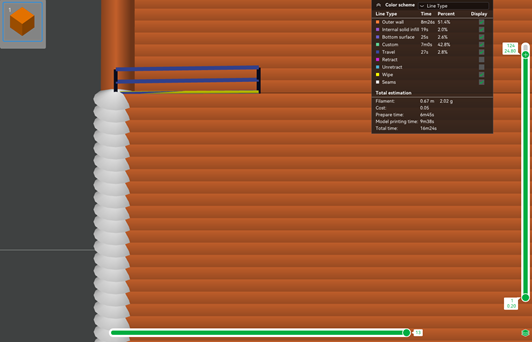 3. Спираль
3. Спираль
- В этом режиме сопло движется вверх и вниз по кругу, сводя к минимуму образование нитей и капель.
 4. Авто
4. Авто
-
В этом режиме, если вы выберете «Авто», принтер автоматически выберет оптимальный способ подъема оси Z. Вот как он принимает это решение:
-
При перемещении внутри одного слоя принтер сначала проверяет, не будет ли движение проходить через нависающие части при подъеме под наклоном. Нависающие части могут увеличиваться и деформироваться во время печати. Подъем под наклоном охватывает более широкую область по осям X и Y, поднимаясь к самой высокой точке, что может привести к столкновению или царапинам на деформированных участках. Если нет риска столкновения, используется подъем под наклоном. Но если есть вероятность столкновения, принтер переключается на спиральный подъем. Спиральная траектория проходит по узкому кругу, охватывая лишь небольшую область непосредственно над напечатанной деталью, поэтому вероятность повреждения меньше.
-
При переходе к новому слою принтер всегда использует метод спирального подъема.
- Скорость ретракции:
- Эта опция определяет скорость втягивания нити.
- Скорость втягивания:
- Эта опция регулирует скорость загрузки филамента в экструдер после ретракции. Установка значения 0 означает, что скорость будет такой же, как и при ретракции.
- Пороговое значение расстояния перемещения
- Чтобы избежать образования нитей в моделях с небольшими зазорами, отрегулируйте пороговое значение расстояния перемещения для втягивания нити. Это позволит соплу втягивать нить только тогда, когда расстояние перемещения превышает этот предел. В противном случае расстояние перемещения может быть слишком коротким для втягивания, и сопло оставит нити между зазорами.
- Втягивание нити при смене слоя:
- Включение этой опции указывает принтеру оттягивать нить перед переходом к новому слою.
- Протирать во время оттягивания нити:
- Эта опция заставляет с�опло перемещаться вдоль предыдущего пути экструзии при втягивании нити. Это может помочь очистить сопло и уменьшить образование нитей и подтекание.
- Расстояние очистки:
- Этот параметр контролирует, насколько далеко сопло перемещается вдоль предыдущего пути экструзии при втягивании нити.
- Втяните нить перед протиркой
- Это величина втягивания сопла перед очисткой, выраженная в процентах от длины втягивания. Значение по умолчанию — 0%, что означает отсутствие втягивания перед очисткой. Это может улучшить шов по оси Z на внешней стенке (если сначала печатается внутренняя стенка).
Теперь мы рассмотрели все настройки втягивания нити в OrcaSlicer, и вы должны знать, как успешно провести тест на втягивание. Если вас интересуют дополнительные процессы калибровки в OrcaSlicer, ознакомьтесь с нашим подробным руководством по методам калибровки OrcaSlicer. В этом руководстве описан ряд методов калибровки.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Что такое тест на втягивание нити в 3D-печати? Тест на втягивание нити — это процесс калибровки, используемый для уменьшения или устранения проблем с образованием нитей и подтеканием материала во время 3D-печати. Он включает в себя систематическое тестирование различных комбинаций расстояния и скорости втягивания нити для поиска оптимальных настроек, которые улучшают качество печати, предотвращая утечку избыточного материала из сопла.
Почему втягивание нити важно в 3D-печати? Втягивание нити имеет решающее значение, поскольку оно предотвращает появление нежелательных нитей или сгустков филамента на поверхности или между частями модели, что влияет на качество и внешний вид печати. Втягивание нити перед перемещением сопла уменьшает поток расплавленного пластика и помогает добиться более чистой и гладкой печати.
Что такое OrcaSlicer и почему его используют для тестирования ретракции? OrcaSlicer — это программное обеспечение для нарезки моделей с открытым исходным кодом, разработанное к�ак форк Bambu Studio для FDM-принтеров. Оно пользуется популярностью для тестирования ретракции благодаря удобному интерфейсу, поддержке различных 3D-принтеров и филаментов, а также таким функциям, как встроенный тест калибровки ретракции, который упрощает настройку параметров ретракции для оптимизации качества печати.
Как выполнить тест на втягивание крючка в OrcaSlicer? Чтобы выполнить тест на втягивание крючка в OrcaSlicer, выполните следующие шаги:
-
Загрузите и установите OrcaSlicer.
-
Выберите принтер, филамент и параметры процесса.
-
Получите доступ к функции проверки ретракции через меню «Калибровка» и отрегулируйте параметры башни ретракции.
-
Настройте длину ретракции в соответствии с типом вашего экструдера.
-
Нарежьте и распечатайте башню ретракции.
-
Проанализируйте результаты, чтобы найти оптимальную длину ретракции.
-
Отрегулируйте параметры филамента в OrcaSlicer с новой длиной ретракции.
Какие ключевые параметры необходимо настроить при тестировании ретракции? Ключевые параметры, которые необходимо настроить во время теста ретракции, включают расстояние ретракции (количество втянутой нити) и скорость ретракции (скорость втягивания нити). Эти параметры необходимо оптимизировать с учетом таких факторов, как тип нити, размер сопла, тип экструдера, скорость печати и температура.
Могут ли настройки ретракции различаться для разных типов филаментов? Да, настройки ретракции могут значительно различаться для разных типов филаментов из-за различий в свойствах материала. Например, для PLA и ABS могут потребоваться разные длины и скорости ретракции. Рекомендуется настраивать параметры ретракции для каждого используемого типа филамента.
Какие советы помогут успешно провести тест на ретракцию? Некоторые советы для успешного проведения теста на ретракцию включают:
-
Выбор оптимального диапазона длин втягивания нити для тестирования.
-
Настройка параметров Z-образного перемещения для предотвращения касания соплом поверхности во время печати.
-
Выравнивание траектории движения непосредственно между двумя точками во избежание образования нитей.
-
Учет типа филаме�нта, поскольку некоторые материалы менее склонны к подтеканию.
Что делать, если после теста на втягивание нити проблемы с образованием нитей сохраняются? Если проблемы с образованием нитей сохраняются после оптимизации настроек втягивания, попробуйте просушить нить, так как влага может повлиять на качество печати. Кроме того, проверьте установку сопла на наличие проблем, которые могут способствовать образованию нитей.
Заключение
В этом руководстве вы узнали, как провести тест на втягивание нити с помощью OrcaSlicer. Это очень важно, если вы хотите значительно улучшить качество своих 3D-отпечатков. Тест на втягивание нити помогает избежать таких проблем, как нити и сгустки на отпечатках. Эти проблемы могут испортить ваши отпечатки, но с правильными настройками втягивания их можно избежать. OrcaSlicer прост в использовании и имеет множество опций. Вы можете сохранить оптимальные настройки втягивания для вашего принтера и филамента. Вы также можете настраивать их для каждого проекта. Если вы будете следовать советам и рекомендациям из этого руководства, вы сможете использовать свой 3D-принтер на полную мощность и гарантировать, что каждый отпечаток будет идеальным.
Also available in: Deutsch | English | Español | Français | Italiano | Nederlands | Polski | Português
