Frustrado com a calibração "subjetiva" da vazão no OrcaSlicer? Este guia rápido ajudará você a abandonar as suposições e dominar objetivamente sua vazão para impressões consistentemente perfeitas.
14 postagens marcadas com "Calibration"
Ver todas os MarcadoresA obtenção de impressões 3D de alta qualidade depende fortemente da calibração precisa da impressora. Sem ela, você encontrará problemas comuns como formação de fios, má adesão da mesa e dimensões imprecisas. A calibração é a base para resultados de impressão consistentes, confiáveis e excelentes.
O OrcaSlicer é um software de fatiamento avançado e de código aberto com poderosas ferramentas de calibração integradas. Este guia ajudará você a usar as versões estáveis mais recentes do OrcaSlicer (normalmente a versão 2.3.0 ou as compilações noturnas recentes da 2.3.1) para ajustar sua impressora. Abordaremos as calibrações de temperatura, vazão, avanço de pressão, retração, tolerância, velocidade volumétrica máxima e artefatos finos verticais (VFA). Esses testes foram projetados para serem realizados em uma ordem específica, melhorando progressivamente a qualidade de impressão.
Compreendendo o OrcaSlicer: seu centro de calibração
O OrcaSlicer oferece recursos avançados como controle preciso de paredes, "modo sanduíche" para melhor acabamento de superfície, "conversão de polifuros" para geometrias complexas e integração perfeita com Klipper, OctoPrint e PrusaLink. Ele oferece controle granular e, ao mesmo tempo, é fácil de usar, com design de arrastar e soltar e perfis de impressora pré-definidos.
Acessando ferramentas de calibração no OrcaSlicer
A maioria dos recursos de calibração está no menu "Calibração". Após concluir qualquer teste de calibração, sempre crie um novo projeto. Isso garante que o OrcaSlicer saia do modo de calibração e redefina os parâmetros para suas próximas impressões.
Ordem de calibração recomendada
Seguir uma ordem de calibração específica é crucial, pois muitas configurações são interdependentes. Começar com parâmetros básicos garante resultados precisos para ajustes subsequentes mais detalhados. Essa abordagem sistemática minimiza a necessidade de solução de problemas e ajuda você a obter melhor qualidade de impressão com eficiência.
| Etapa de Calibração | Objetivo | Observação/Objetivo Principal | Dependência/Pré-requisito |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura | Otimizar a fusão e a ligação do filamento | Menor formação de filamentos, melhor adesão de camadas | Nenhum (assume boa configuração mecânica) |
| Taxa de Fluxo | Garantir a quantidade correta de extrusão do filamento | Superfície superior mais lisa, sem lacunas ou bolhas | Temperatura, Etapas E/Distância de Rotação Precisas |
| Avanço de Pressão | Reduzir artefatos de flutuações de pressão do bico | Cantos mais afiados, extrusão consistente | Taxa de Fluxo, Temperatura |
| Retração | Minimizar a formação de filamentos e o escoamento | Menor comprimento com formação mínima de filamentos | Taxa de Fluxo, Avanço de Pressão |
| Tolerância | Reproduzir com precisão as dimensões do modelo | Encaixe ideal entre as peças impressas | Todas as calibrações dimensionais/de extrusão anteriores |
| Velocidade Volumétrica Máxima | Determinar a taxa de fluxo máxima do filamento sem problemas | Maior velocidade antes da subextrusão | Temperatura, Taxa de fluxo |
| Curvas/Solavancos/Desvio de junção | Redução de artefatos de cantos vivos | Cantos mais suaves, redução de zumbido | Taxa de fluxo, Avanço de pressão |
| Moldagem de entrada | Redução de zumbido e melhoria da qualidade de impressão | Superfícies mais suaves, redução de fantasmas | Taxa de fluxo, Avanço de pressão |
Tabela 1: Ordem de calibração recomendada do OrcaSlicer
Calibração básica da impressora: antes de fatiar
Antes de usar as ferramentas avançadas do OrcaSlicer, certifique-se de que os sistemas mecânicos e térmicos fundamentais da sua impressora estejam configurados. Essas etapas geralmente são realizadas diretamente no firmware da impressora ou por meio de ajustes físicos, e não no OrcaSlicer. Ignorá-las pode causar problemas persistentes na qualidade da impressão.
Calibração de deslocamento Z: crítica para as primeiras camadas
O deslocamento Z define a distância precisa entre o bico e a plataforma de impressão para a primeira camada. É fundamental para a adesão à plataforma. Se o bico estiver muito alto, o filamento não grudará; se estiver muito baixo, pode raspar a plataforma, causar "pé de elefante" ou causar cliques na extrusora.
Este é principalmente um ajuste físico ou de firmware da impressora. Embora o OrcaSlicer tenha um campo de deslocamento Z (em Predefinições da impressora > guia Geral), entenda como o firmware da sua impressora lida com isso. A maioria das impressoras depende de ajustes físicos ou de firmware. Sempre execute a calibração de deslocamento Z na sua impressora primeiro. Use a configuração do OrcaSlicer apenas para pequenos ajustes se a sua impressora permitir o deslocamento Z definido pelo fatiador.
Nivelamento da cama: garantindo uma base perfeita
Uma cama de impressão nivelada garante uma adesão consistente da primeira camada em toda a superfície. Uma cama irregular faz com que algumas áreas adiram bem e outras se levantem. A OrcaSlicer oferece a "Malha Adaptável da Cama" para compensar pequenas imperfeições, mapeando a cama.
A malha adaptável da cama da OrcaSlicer é uma ferramenta de software, não um substituto para uma cama mecanicamente sólida e inicialmente nivelada. Confiar apenas em software sem nivelamento manual ou assistido inicial (por exemplo, método de papel) pode mascarar problemas mecânicos. Se a cama estiver significativamente deformada, a malha pode apresentar dificuldades. Primeiro, nivele a cama mecanicamente, depois defina o deslocamento Z e, por fim, deixe o nivelamento automático da impressora ou a malha adaptável da cama da OrcaSlicer fazer o ajuste fino.
E-steps / Calibração de distância de rotação: o herói anônimo
Antes de ajustar a vazão no fatiador, certifique-se de que os passos E (Marlin) ou a distância de rotação (Klipper) da sua extrusora estejam calibrados. Isso indica à sua impressora a quantidade de filamento a ser empurrada. Se a calibração estiver incorreta, a impressora extrudará a quantidade errada, tornando a calibração da vazão do fatiador imprecisa. Esta é uma calibração de firmware da impressora, não uma configuração do OrcaSlicer.
Testes de calibração de núcleo no OrcaSlicer
Depois que as configurações básicas da impressora forem feitas, use os testes de calibração integrados do OrcaSlicer para otimizar a qualidade de impressão.
1. Calibração de temperatura: Encontrando o ponto ideal do seu filamento
A temperatura afeta a forma como o filamento derrete, flui e se liga. Temperaturas muito baixas causam subextrusão, baixa adesão e peças fracas. Temperaturas muito altas causam vazamentos, formação de fios, deformações e bolhas.
A calibração precisa da temperatura depende do deslocamento Z prévio, do nivelamento da mesa e do ajuste do PID. Se estes estiverem incorretos, os resultados da torre de temperatura podem ser enganosos. Certifique-se de que sua impressora esteja mecanicamente em boas condições e com o PID ajustado antes de executar testes de temperatura para obter resultados precisos.
Passo a passo: usando a torre de temperatura integrada do OrcaSlicer
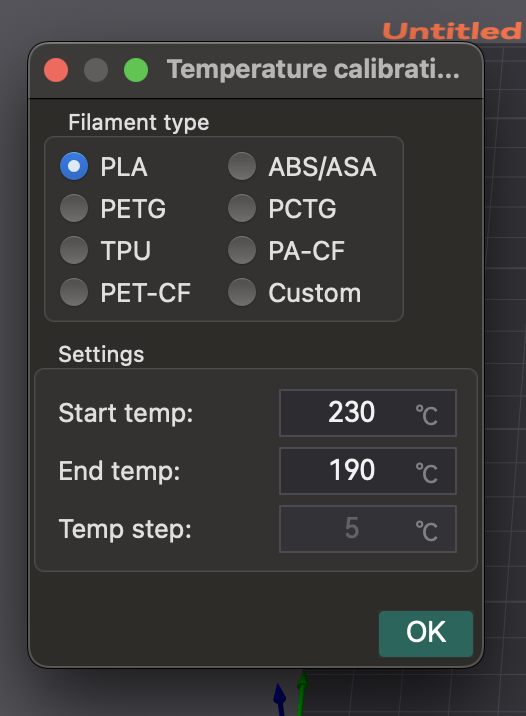
- Preparação: No OrcaSlicer, selecione o material (PLA, PETG, etc.). Isso define as faixas de temperatura padrão da cama e do bico. Acesse "Calibração" > "Temperatura". Defina as temperaturas inicial/final personalizadas (o incremento é fixo em 5 °C).
- Imprimindo a Torre: O OrcaSlicer gera uma torre de temperatura. Fatie e imprima.
- Analisando os Resultados: Após a impressão, inspecione cada camada quanto à formação de cordões, adesão de camadas, deformações e desempenho de saliência/ponte. Encontre o bloco de temperatura com a melhor qualidade geral de impressão e o menor número de defeitos.
- Aplicando Configurações: Atualize a temperatura ideal do bico nas configurações do seu perfil de filamento no OrcaSlicer. Salve o perfil e crie um novo projeto.
A temperatura é específica para cada filamento. Diferentes marcas ou cores do mesmo tipo de filamento podem ter diferentes faixas ideais. Realize este teste para cada novo filamento para criar uma biblioteca de perfis ajustados.
Solução de problemas: problemas comuns relacionados à temperatura
- Encordoamento/Escorrimento: geralmente significa que a temperatura está muito alta ou que as configurações de retração estão incorretas.
- Má adesão da camada/Subextrusão: a temperatura do bico costuma estar muito baixa.
- Deformação: pode ser devido a temperaturas incorretas da base/bico ou resfriamento insuficiente.
| Tipo/Marca de Filamento | Faixa de Temperatura Testada | Temperatura Ideal | Principais Observações na Temperatura Ideal |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA (Genérico) | 190-230°C | 205°C | Mínimo encordoamento, forte adesão entre camadas, boas saliências |
| PETG (Prusament) | 230-250°C | 240°C | Superfície lisa, sem empenamento, boa ligação em ponte |
| ABS (Hatchbox) | 230-260°C | 245°C | Menor formação de trincas, boa ligação entre camadas |
Tabela 2: Configurações e observações da torre de temperatura
2. Calibração da taxa de fluxo: alcan�çando precisão dimensional
A vazão (multiplicador de extrusão) controla a quantidade de filamento extrudado. É crucial para superfícies lisas e precisão dimensional. Se for muito alta, ocorre superextrusão: bolhas, formação de fios, baixa precisão. Se for muito baixa, ocorre subextrusão: lacunas, adesão fraca, acabamento ruim.
A calibração da vazão depende muito da temperatura e dos passos E/distância de rotação. Se a sua extrusora não estiver calibrada, os ajustes da vazão no fatiador serão imprecisos. Certifique-se primeiro de que os passos E estejam corretos e a temperatura esteja ideal.
A altura da camada e a velocidade de impressão também podem afetar a vazão ideal. Se os limites de velocidade de impressão mudarem, execute a calibração novamente.
Passo 1: Calibração Inicial
- Criando o Projeto de Teste: No OrcaSlicer, selecione as configurações da impressora, do filamento e do processo. Vá em "Calibração" > "Passo 1". Isso gera nove blocos, cada um com um modificador de vazão diferente.
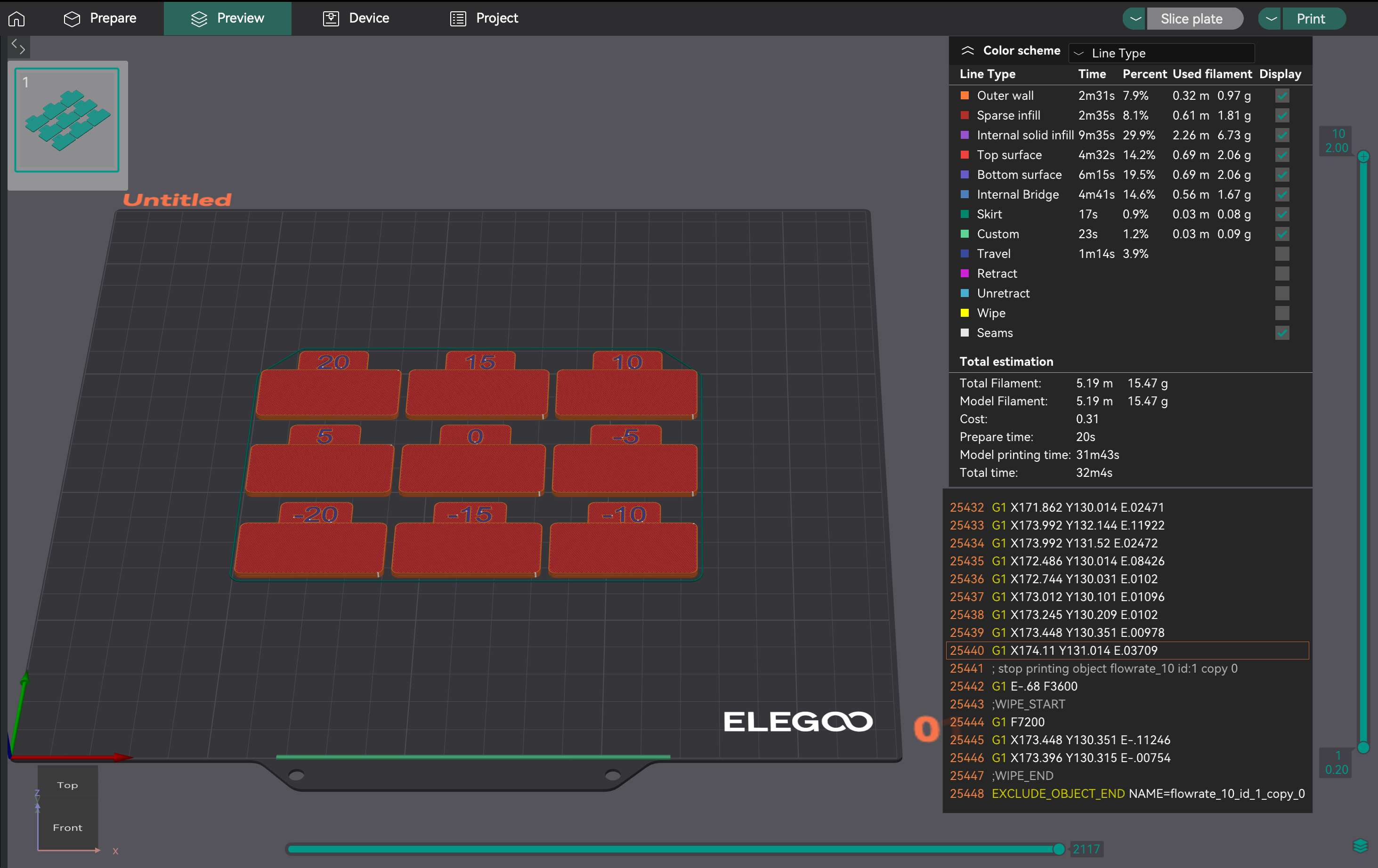
- Analisando a Superfície Mais Lisa: Imprima o projeto. Examine as superfícies superiores. Encontre o bloco com a superfície mais lisa, livre de sobreextrusão (sulcos, bolhas) ou subextrusão (lacunas). Se dois forem semelhantes, escolha aquele com a maior vazão.
- Calculando a Taxa de Vazão: Calcule Taxa_de_Vazão_nova = Taxa_de_Vazão_antiga * (100 + modificador) / 100. Exemplo: 0,98 * (100 + 5) / 100 = 1,029.
Passo 2: Ajuste fino para a perfeição
- Gerando o Projeto de Ajuste Fino: Crie um novo projeto. Vá em "Calibração" > "Passo 2". Isso gera dez blocos com modificadores de -9 a 0 para ajustes precisos.
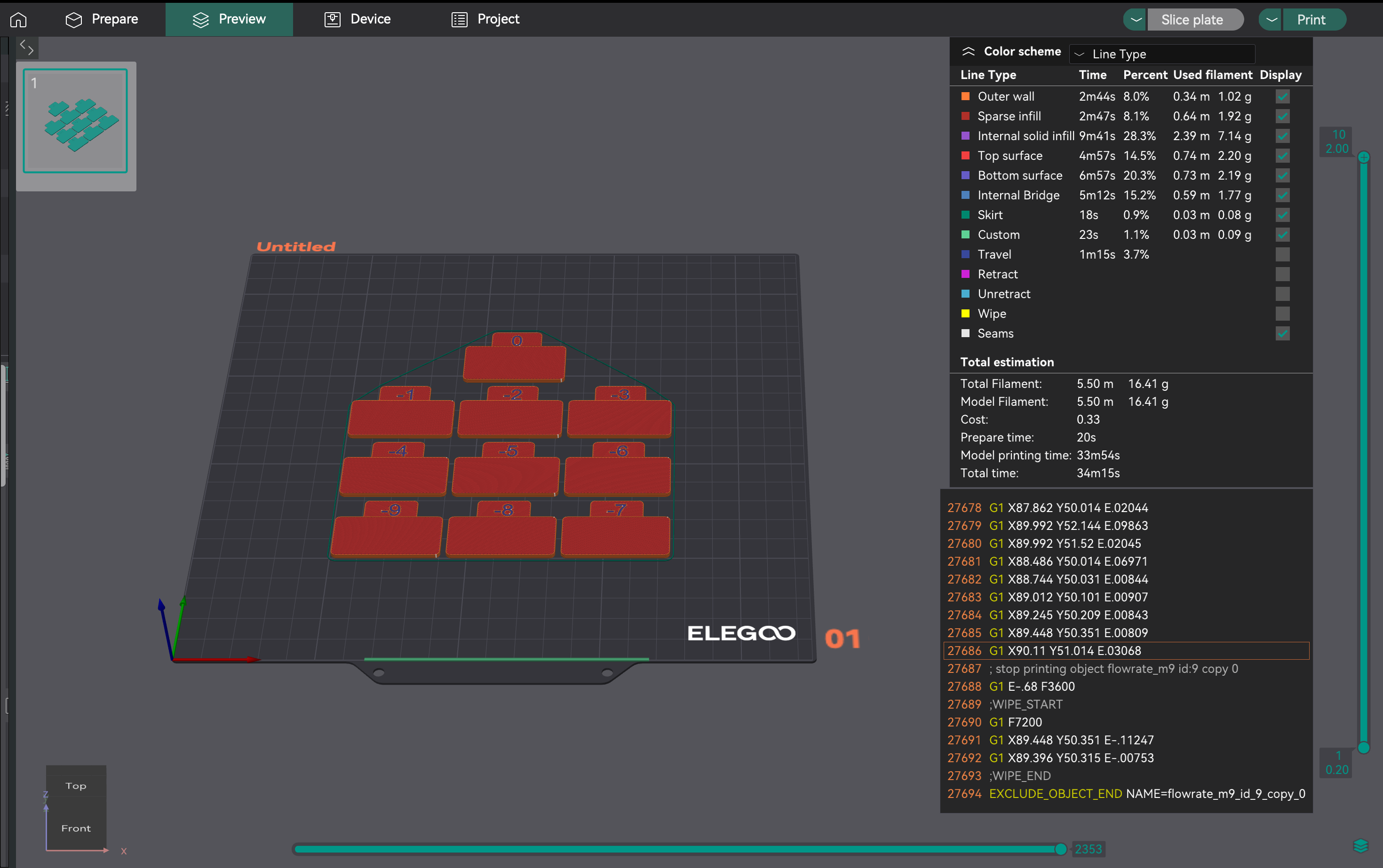
- Avaliando a Consistência: Imprima o Passo 2. Examine as superfícies superiores para obter a melhor qualidade, adesão das camadas e consistência. Calcule a taxa de fluxo atualizada usando a mesma fórmula. Exemplo: 1,029 * (100 - 6) / 100 = 0,96726.
- Aplicando as Configurações: Salve a taxa de fluxo ideal final nas configurações do seu perfil de filamento no OrcaSlicer.
Solução de problemas de calibração de fluxo integrada do OrcaSlicer: Orientação sobre "Metacalibração"
Você pode achar os resultados da calibração de fluxo integrada do OrcaSlicer "terríveis" e exigir intervenção manual. Isso indica a necessidade de orientação de "metacalibração": como solucionar problemas no próprio processo de calibração.
-
Extrusão excessiva/arrasto inicial: Isso pode significar que a temperatura de impressão está muito alta ou que os passos E/distância de rotação não estão calibrados. Verifique novamente os passos E antes de executar novamente a calibração de fluxo.
-
Clique na extrusora: Muitas vezes significa que a temperatura está muito baixa para o fluxo desejado, fazendo com que o motor da extrusora falhe. Aumente ligeiramente a temperatura do bico ou diminua a velocidade volumétrica máxima (abordada posteriormente) antes de tentar novamente a calibração de fluxo.
-
Inconsistência/Resultados ambíguos do teste: Se as impressões de calibração parecerem ruins, mas outras impressões estiverem boas, considere:
-
Velocidade de impressão do teste: A velocidade padrão pode estar muito alta. Tente diminuir a velocidade das impressões de calibração.
-
Configurações de largura de linha: Se a largura da linha (nas configurações do processo) for muito grande para o seu bico, isso pode causar extrusão excessiva. Certifique-se de que as larguras sejam adequadas (por exemplo, 0,45 mm para um bico de 0,4 mm).
-
Subjetividade do Teste Visual: A avaliação visual pode ser subjetiva. Para resultados mais objetivos, imprima um cubo de parede única:
- Imprima um cubo de parede única (por exemplo, 20x20x20 mm, 0% de preenchimento, 1 perímetro).
- Meça a espessura da parede com um paquímetro.
- Calcule a espessura de parede desejada (por exemplo, 0,4 mm para um bico de 0,4 mm).
- Ajuste a taxa de fluxo: Nova taxa de fluxo = Taxa de fluxo atual * (Espessura de parede desejada / Espessura de parede medida).
- Persistência de problemas: Se a calibração de fluxo falhar consistentemente, uma calibração anterior (temperatura, passos E/distância de rotação ou problemas mecânicos) provavelmente ainda está incorreta. Não prossiga para Avanço ou Retração de Pressão até que o fluxo esteja regulado de forma confiável.
| Aprovado | Faixa do Modificador | Número de Blocos | Fórmula de Cálculo | Finalidade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aprovado 1 | +5 a -5 | 9 | Nova Taxa de Fluxo = Antiga Taxa de Fluxo * (100 + modificador) / 100 | Calibração inicial para encontrar a faixa ideal aproximada |
| Aprovado 2 | -9 a 0 | 10 | Nova Taxa de Fluxo = Antiga Taxa de Fluxo * (100 + modificador) / 100 | Ajuste fino para uma taxa de fluxo ideal precisa |
Tabela 3: Resumo das passagens 1 e 2 da calibração da vazão
3. Calibração de avanço de pressão: afiando seus cantos
O Avanço de Pressão (PA) compensa as variações de pressão no bico durante as flutuações de velocidade (aceleração/desaceleração). Ele previne cantos arredondados, bolhas e "espinhas" pré-ajustando a extrusão para manter o fluxo uniforme.
Sempre realize a calibração de Avanço de Pressão após a calibração da Taxa de Fluxo. Se a taxa de fluxo estiver incorreta, a PA compensará de forma imprecisa. Uma taxa de fluxo estável é essencial para uma PA eficaz. Se os seus testes de PA parecerem confusos, reveja as calibrações de Taxa de Fluxo e Temperatura primeiro.
Os valores de PA variam significativamente de acordo com o tipo de extrusora (Direct Drive vs. Bowden), tipo/marca de filamento, tamanho do bico, temperatura do hotend e modificações de hardware. Diferentes materiais têm um fluxo de fusão único, e as alterações no comprimento do caminho de fluxo afetam o PA. Isso significa que o PA frequentemente requer recalibração para diferentes configurações ou materiais.
Escolhendo a configuração da sua extrusora (Direct Drive vs. Bowden)
O OrcaSlicer solicita que você selecione o tipo de extrusora (Direct Drive ou Bowden). Os valores de PA variam bastante devido ao comprimento do caminho do filamento. Configurações Bowden geralmente exigem valores de PA mais altos.
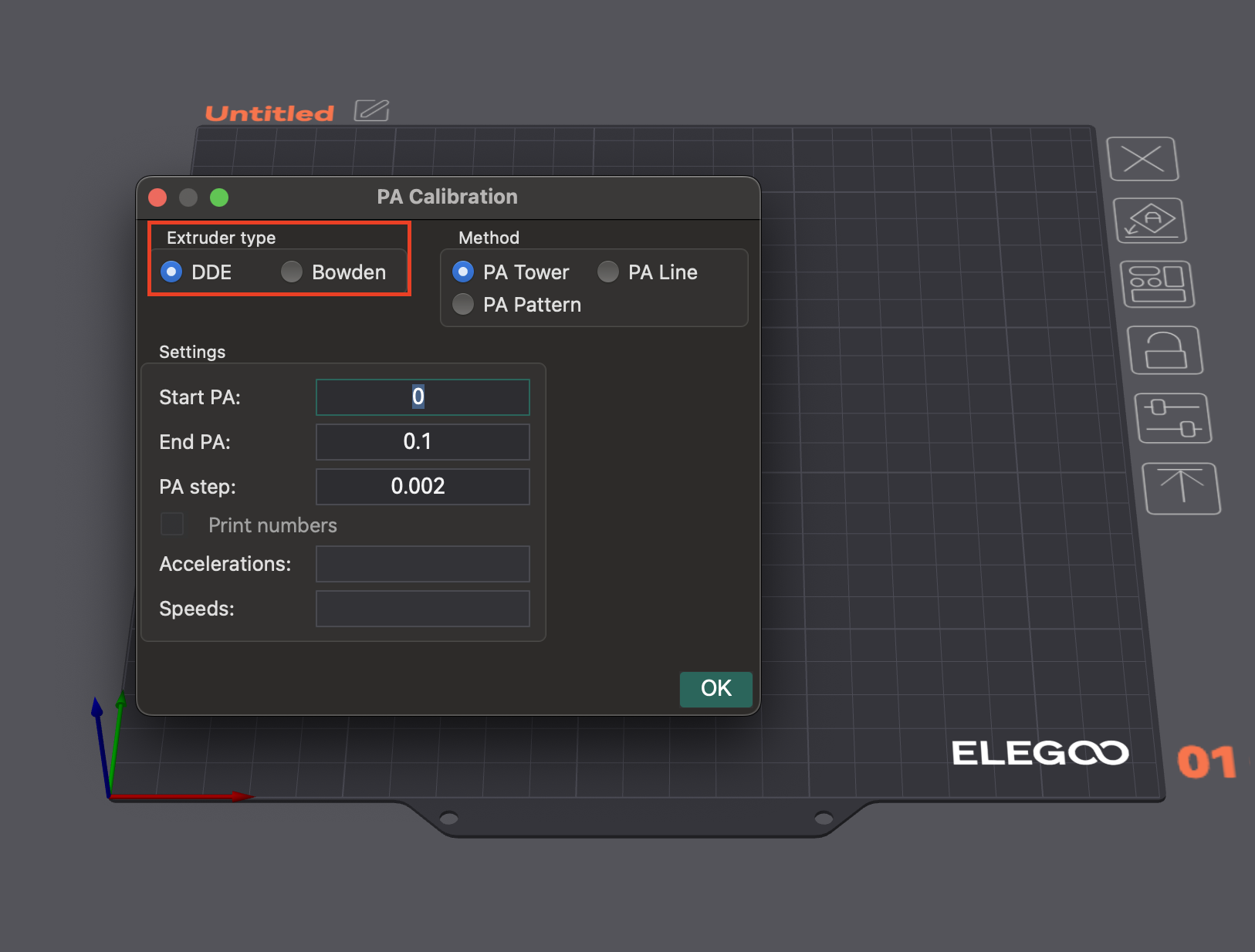
Métodos no OrcaSlicer
O OrcaSlicer oferece vários métodos para calibração de avanço de pressão:
- Método da Linha: Este método ajuda a identificar rapidamente um valor ideal de Avanço de Pressão.
- Acesso: Acesse "Calibração" > "Avanço de Pressão" > "Linha PA".
- Teste: O OrcaSlicer gera uma série de linhas, cada uma impressa com um valor de PA incrementalmente diferente. O objetivo é observar onde o início e o fim de cada linha parecem mais "limpos" e a transição para dentro e para fora da linha é mais nítida, indicando a extrusão mais consistente.
- Dependência: Este método é sensível à qualidade da primeira camada. Certifique-se de que sua base esteja devidamente nivelada antes de realizar este teste.
- Método do Padrão: Avaliação visual dos cantos.
- Acesso: No menu "Calibração", selecione "Avanço de Pressão" e, em seguida, escolha o "Método do Padrão".
- Teste: O OrcaSlicer gera um padrão semelhante a um prisma. Verifique a consistência da qualidade da extrusão e identifique os cantos mais nítidos com menos artefatos (como vãos, saliências ou depressões).
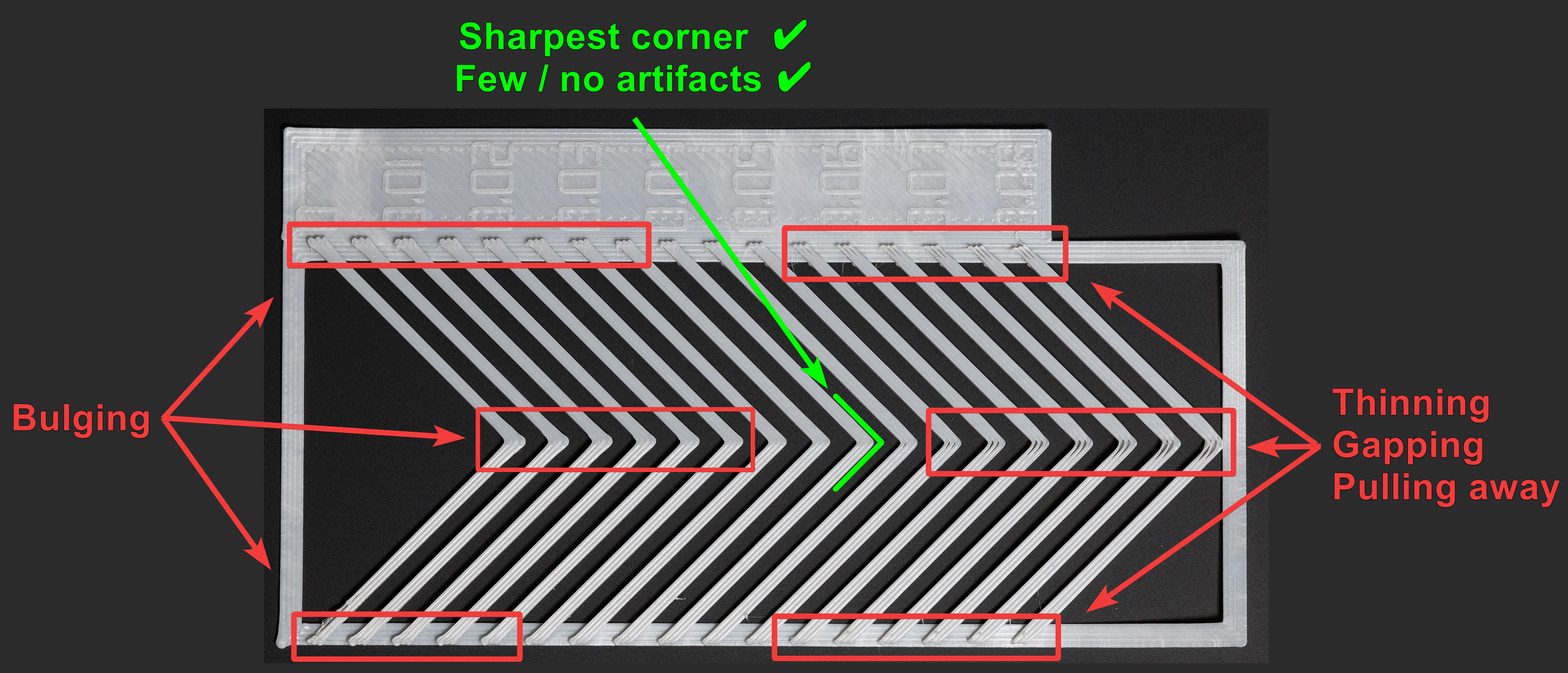
Fonte: obico.io 3. Método da Torre: Menos sensível à qualidade da primeira camada, mas leva mais tempo.
- Acesso: No menu "Calibração", selecione "Avanço de Pressão" e, em seguida, escolha "Torre PA".
- Teste: O software gera uma torre onde a PA aumenta com a altura (tipicamente 0,002 por mm para Direct Drive, 0,02 para Bowden). Examine cada canto para encontrar a altura com cantos nítidos e limpos.
- Recomendação: Imprima em velocidades mais altas (acima de 120 mm/s) para verificar o impacto da PA em condições típicas de impressão.

Fonte: ellis3dp.com
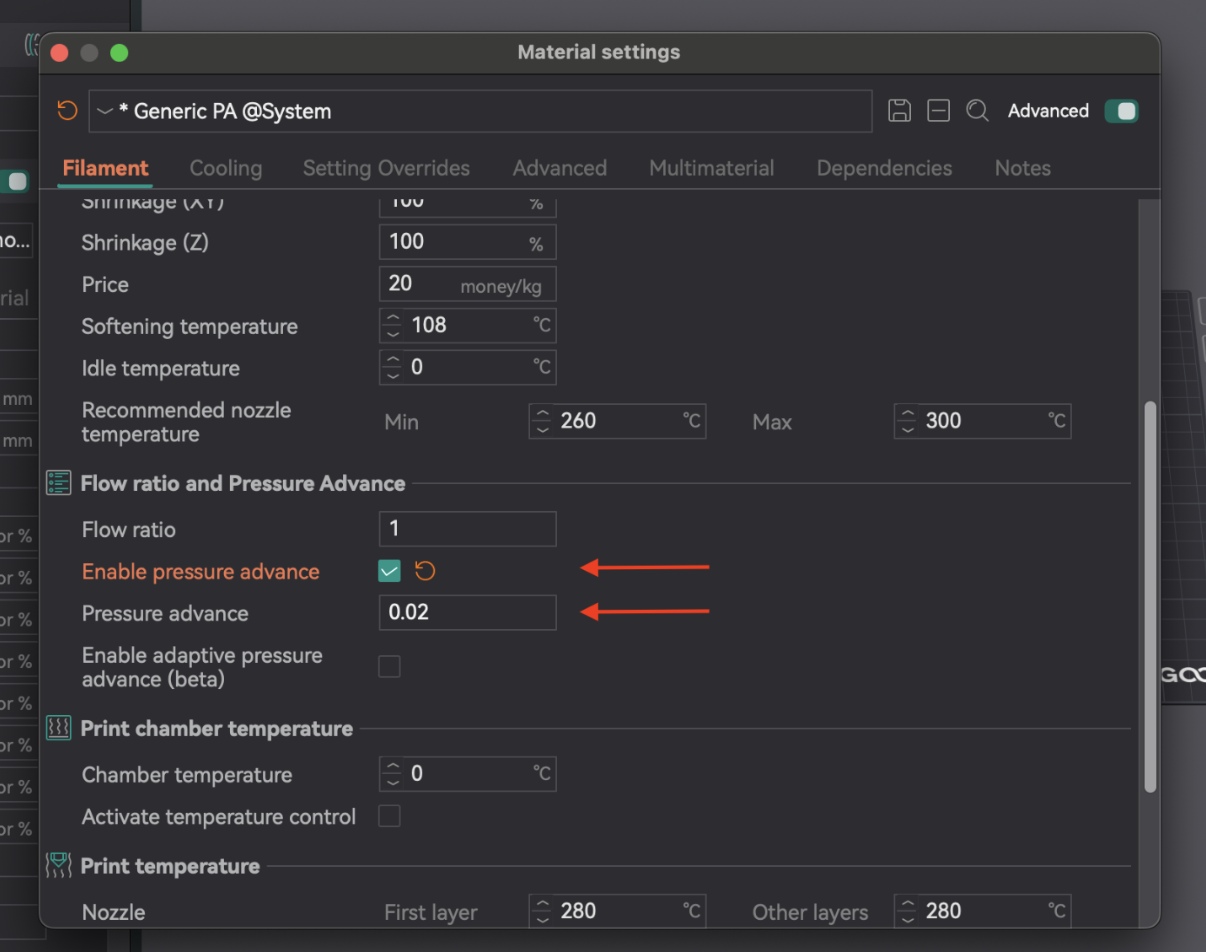
Aplicando configurações no OrcaSlicer
Após determinar o valor ideal de PA, abra as configurações do filamento (ícone de edição ao lado do perfil). Ative "Ativar avanço de pressão" e insira o valor. Salve o perfil do filamento.
| Método | Tipo de Extrusora | Prós | Contras | Observação Principal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linha | Ambas | Rápido, simples de testar | Altamente dependente da qualidade da primeira camada | Extremidades de linha mais limpas, ponta mais afiada |
| Padrão | Ambas | Avaliação visual dos cantos, mais avançada | Ainda um pouco dependente da primeira camada | Extrusão mais consistente, canto mais afiado com menos artefatos |
| Torre | Ambas | Menos sensível à qualidade da primeira camada, bom para altas velocidades | Consome mais tempo e material | Melhor qualidade geral dos cantos em uma altura específica |
Tabela 4: Comparação do método de avanço de pressão
4. Calibração de retração: eliminando a formação de fios e vazamentos
A retração puxa o filamento para trás antes do movimento de deslocamento, criando pressão negativa para evitar vazamentos, fios ou bolhas. Os principais parâmetros são o comprimento da retração, a velocidade e o salto Z.
A retração interage com o avanço da pressão. A retração ideal ajuda a controlar o recuo físico, enquanto o PA lida com a pressão no hotend. Se o PA não estiver calibrado, a retração pode apresentar dificuldades. O objetivo é obter o menor comprimento possível que minimize o encordoamento sem causar obstruções ou "marcas de buraco".
Se a formação de cordas persistir após os testes de retração, reavalie primeiro as configurações de temperatura e vazão e, depois, o avanço de pressão. Essas configurações básicas devem estar corretas para que a retração seja eficaz.
Passo a passo: usando o teste de retração integrado do OrcaSlicer
- Acessar e Configurar: Crie um novo projeto. Acesse "Calibração" > "Teste de Retração". Configure "Comprimento inicial de retração", "Comprimento final de retração" e "Passo" (padrões normalmente 0 mm, 2 mm, 0,1 mm). Extrusoras Bowden geralmente precisam de comprimentos maiores (1-6 mm) do que o acionamento direto (0-2 mm).
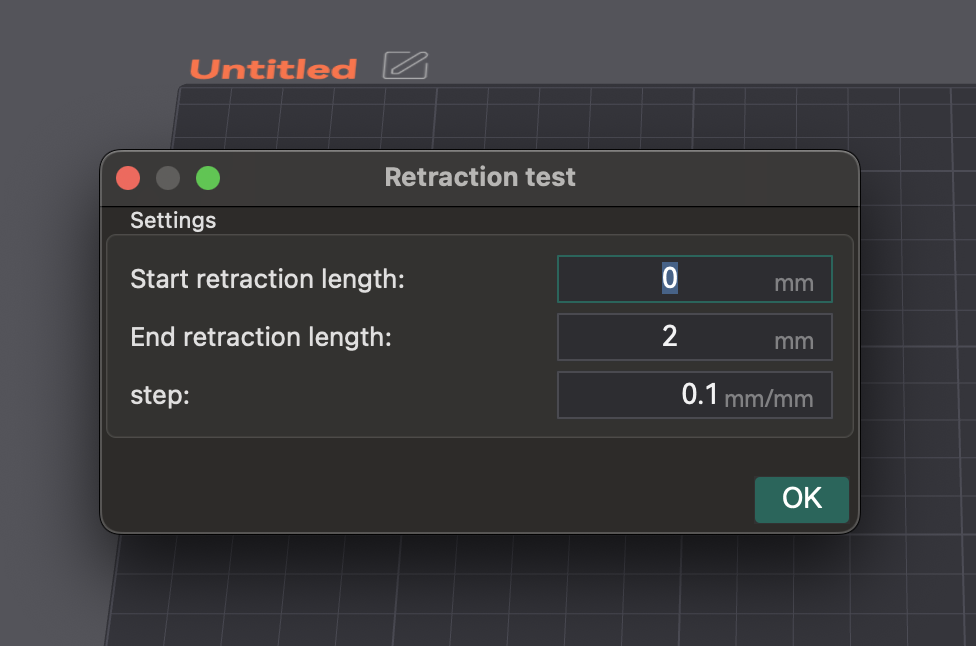
- Fatiar e Imprimir: Fatie e imprima a torre de retração. Certifique-se de que a opção Z-hop "Normal" esteja selecionada. Você pode pintar as costuras nas laterais internas da torre na pré-visualização para uma observação mais clara das linhas.
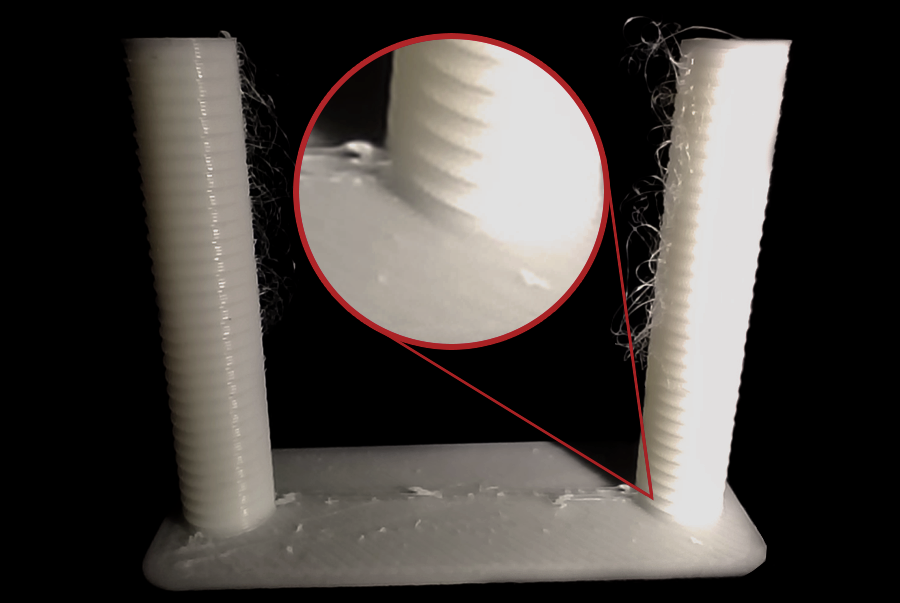
Fonte: obico.io
3. Analisando os Resultados e Ajustando: Examine cada entalhe. Encontre o menor comprimento que minimize a formação de fios e o escoamento sem outros problemas. Exemplo: se a melhor qualidade for um entalhe da base com passo de 0,1 mm, o comprimento ideal é 0,2 mm. Abra as configurações do filamento, aba "Substituições de Configurações", marque "comprimento" em retração, insira o novo valor e salve.
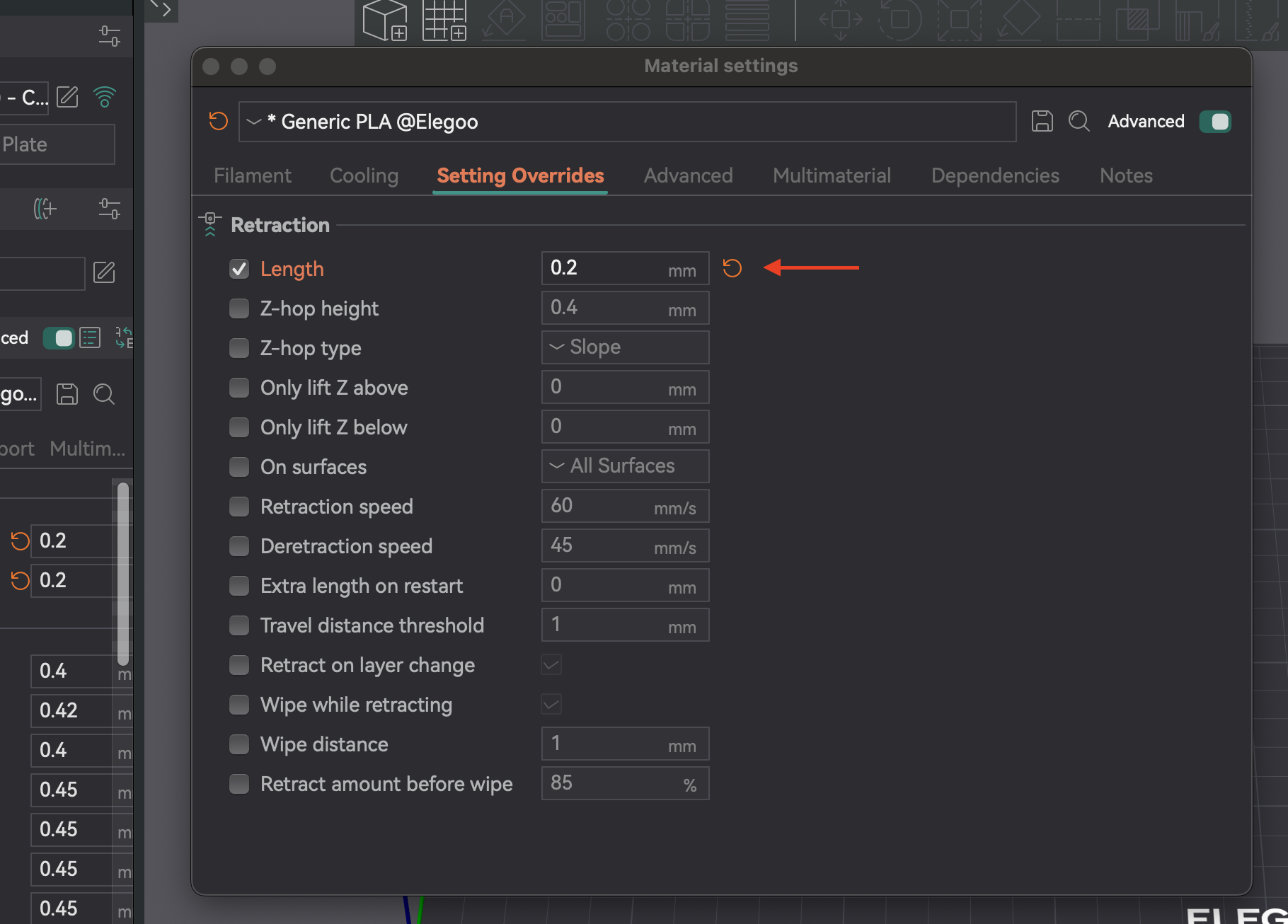
Solução de problemas: formação persistente de fios, vazamentos e entupimentos nos bicos
- Tipo de Filamento: Diferentes materiais apresentam diferentes escoamentos. PLA/ABS normalmente necessitam de menor retração (0,2-0,4 mm) do que filamentos flexíveis ou higroscópicos.
- Secagem do Filamento: A umidade é uma causa comum de formação de fios. Se o escoamento persistir, seque o filamento. Geralmente, esta é a primeira coisa a verificar.
- Instalação do Bico: Um bico solto ou parcialmente obstruído pode causar formação de fios. Verifique a instalação e remova obstruções regularmente.
- Limpeza durante a retração: Esta configuração faz com que o bico se mova durante a retração, limpando-o e reduzindo a formação de fios/escorrimento.
- Velocidade de Desretração: Controla a velocidade de recarga após a retração. Definir como 0 utiliza a velocidade de retração.
- Limite de Distância de Percurso: Retrai somente se o percurso exceder um limite, evitando retrações desnecessárias e reduzindo a formação de fios em pequenos espaços.
| Configuração | Descrição | Problema comum | Solução/Dica |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comprimento de retração | Quantidade de filamento puxado para trás. | Enfiamento, vazamento, obstruções (se muito alto) | Aumente para enfiamento, diminua para obstruções/marcas. |
| Velocidade de retração | Velocidade de retração do filamento. | Enfiamento, bolhas, trituração do filamento | Aumente para uma resposta mais rápida, evite trituração. |
| Z-Hop | Levanta o bico durante o deslocamento. | Bico raspando, bolhas na superfície | Habilite para impressões complexas, ajuste a altura. |
| Velocidade de desretração | Velocidade para recarregar o filamento. | Subextrusão no início de uma nova linha | Defina como 0 (usa a velocidade de retração) ou um pouco menos. |
| Limite de distância de deslocamento | Percurso mínimo para retração. | Enfiamento em pequenos espaços | Ajuste para ativar para o deslocamento relevante. |
| Limpar durante a retração | O bico se move ao longo do caminho durante a retração. | Visibilidade da costura em Z, vazamento | Habilita para melhorar as costuras da parede externa e reduzir o vazamento. |
Tabela 5: Configurações de retração e solução de problemas
5. Teste de tolerância: garantindo o encaixe perfeito das peças
Tolerância é a precisão com que sua impressora reproduz as dimensões. Ela é crucial para peças que se encaixam (montagens, componentes de encaixe). Variações dimensionais decorrem da contração do filamento e da mecânica da impressora. O teste de tolerância ajuda você a entender o comportamento da sua impressora para ajustar os designs e obter encaixes perfeitos.
A tolerância é uma característica da combinação filamento-impressora. Não se trata de uma configuração única. Filamentos diferentes encolhem de forma diferente, e até mesmo marcas/cores podem variar. Teste novamente ao trocar de tipo ou marca de filamento ou ao fazer modificações significativas no hardware. Mantenha os perfis por filamento para uma precisão consistente.
Usando o teste de tolerância integrado do OrcaSlicer
- Acesso: Vá em "Calibração" > "Teste de tolerância Orca". Isso abrirá um novo projeto com o modelo de teste.
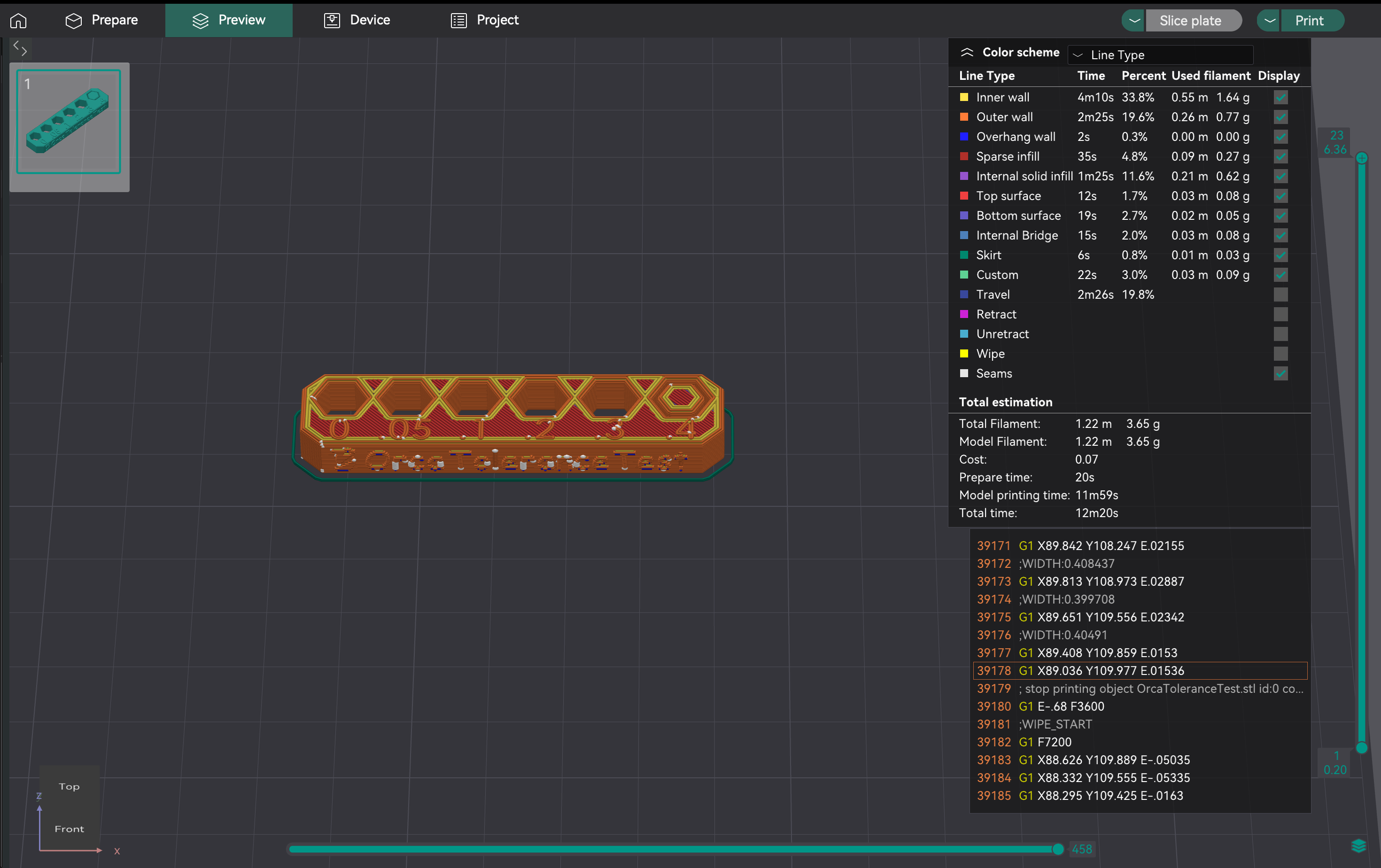
- Descrição do Modelo: O modelo possui uma base com seis furos hexagonais (tolerâncias de 0,0 mm, 0,05 mm, 0,1 mm, 0,2 mm, 0,3 mm e 0,4 mm) e um testador hexagonal.
- Impressão: Selecione as configurações da impressora, do filamento e do processo. Fatie e imprima.
- Importante: Evite usar a compensação de furos X-Y e a compensação de contornos X-Y (definidas como 0 mm) durante este teste, pois elas podem distorcer os resultados.
Analisando resultados com uma chave Allen ou testador impresso: Encontrando o ajuste "perfeito"
Após a conclusão da impressão, use uma chave Allen M6 ou o testador hexagonal impresso incluso. Seu objetivo é identificar o menor orifício na impressão de teste em que o testador possa deslizar com o mínimo ou nenhuma força, e sem qualquer oscilação ou folga perceptível. Este orifício específico representa a saída real da sua impressora para um encaixe "confortável" ou "suave" com aquele filamento.
Veja como determinar objetivamente esse ajuste "perfeito":
- Comece pelos furos menores: Comece tentando inserir o testador nos furos de 0,0 mm, 0,05 mm e 0,1 mm.
- Avalie o encaixe para cada um:
- Muito apertado: Se você precisar forçar o testador ou se ele simplesmente não entrar, o furo está muito apertado para um encaixe "perfeito".
- Muito frouxo/instável: Se o testador entrar com muita facilidade e apresentar folga perceptível ou se mover, o furo está muito frouxo para um encaixe "perfeito".
- Perfeito: Este é o furo mais apertado, onde o testador entra suavemente, exigindo uma pressão leve, mas consistente, e apresenta pouca ou nenhuma folga perceptível após a inserção.
- O tamanho indicado para este furo "exatamente certo" (por exemplo, 0,1 mm, 0,2 mm ou 0,3 mm) indica a precisão dimensional inerente da sua impressora para furos com aquele filamento específico. Este valor observado é crucial para determinar como aplicar a compensação para atingir o ajuste desejado em projetos futuros.
Fonte: hta3d.com
Ajustando a compensação de furo/contorno X-Y
Depois de identificar o ajuste "perfeito" na impressão do teste de tolerância (por exemplo, o furo de 0,2 mm se encaixa perfeitamente no teste), você usará essa observação para ajustar a compensação de furos X-Y no OrcaSlicer. Essa configuração será aplicada a todos os furos em seus projetos futuros para garantir que eles sejam impressos com o ajuste desejado.
- Cenário 1: Seus furos impressos estão consistentemente saindo menores do que o projetado (muito apertados).
- Exemplo: Você projeta uma peça com um furo de folga de 0,2 mm esperando um encaixe "perfeito". Na impressão do teste de tolerância, o furo de 0,2 mm está muito apertado e o testador só encaixa suavemente no furo de 0,3 mm. Isso indica que sua impressora está fazendo furos aproximadamente 0,1 mm menores do que o projetado.
- Ação: Você precisa aumentar a compensação do furo X-Y com um valor positivo. Neste exemplo, definir a compensação do furo X-Y para +0,1 mm faria com que todos os furos em suas impressões futuras fossem impressos 0,1 mm maiores, fazendo com que os furos de folga de 0,2 mm projetados ficassem mais próximos do encaixe "perfeito".
- Cen�ário 2: Seus furos impressos estão consistentemente saindo maiores do que o projetado (muito frouxos).
- Exemplo: Você projeta uma peça com um furo de folga de 0,2 mm esperando um encaixe "perfeito". No seu teste de tolerância, o furo de 0,2 mm está muito frouxo e o testador só se encaixa suavemente no furo de 0,1 mm. Isso indica que a sua impressora está fazendo furos aproximadamente 0,1 mm maiores do que o projetado.
- Ação: Você precisa diminuir a compensação do furo X-Y com um valor negativo. Neste exemplo, definir a compensação do furo X-Y para -0,1 mm faria com que todos os furos em suas impressões futuras fossem impressos 0,1 mm menores, fazendo com que os furos de folga de 0,2 mm projetados ficassem mais próximos do encaixe "perfeito".
Lembre-se de que a compensação de furos X-Y é específica para características internas, como furos. A compensação de contorno X-Y é usada para ajustar as dimensões externas gerais da sua peça e normalmente não é ajustada com base nos resultados deste teste específico de tolerância de furo.
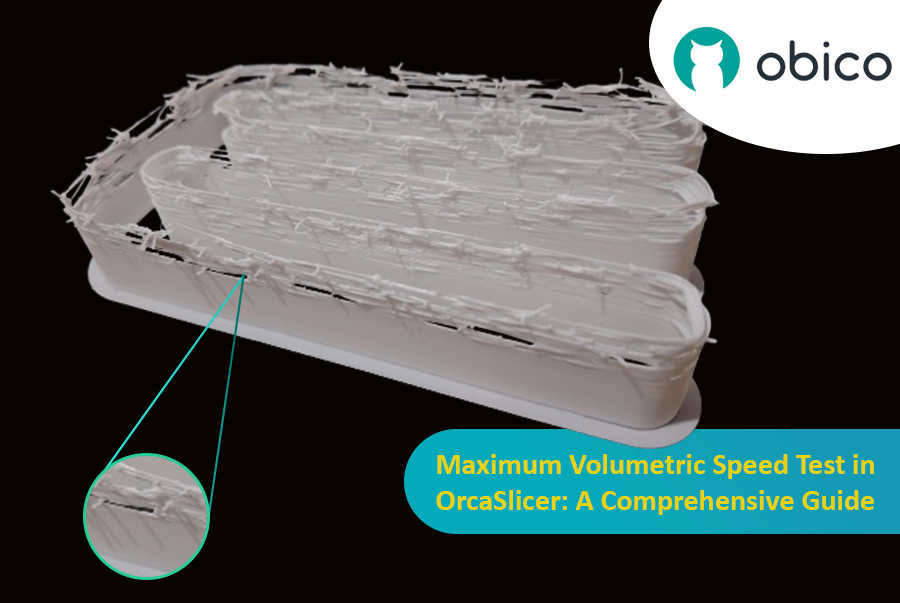
6. Calibração de velocidade volumétrica máxima: ultrapassando os limites da sua impressora
A velocidade volumétrica máxima (ou vazão máxima) é o maior volume de filamento (mm³/s) que seu hotend consegue fundir e extrudar consistentemente sem problemas. Isso garante que sua impressora possa lidar com o fluxo comandado, especialmente em altas velocidades, sem subextrusão (o hotend não consegue fundir rápido o suficiente) ou superextrusão (pressão excessiva). Determinar esse limite otimiza as velocidades de impressão sem sacrificar a qualidade.
A velocidade volumétrica máxima é um limite para o hotend e o filamento. Filamentos diferentes têm taxas de fluxo de fusão únicas. PLA, PETG e ABS terão valores máximos diferentes. Você deve testar cada tipo de filamento que planeja imprimir em altas velocidades para definir configurações específicas de velocidade volumétrica em cada perfil de filamento.
Como realizar o teste no OrcaSlicer
- Acesso: Vá em "Calibração" > "Velocidade Volumétrica Máxima".
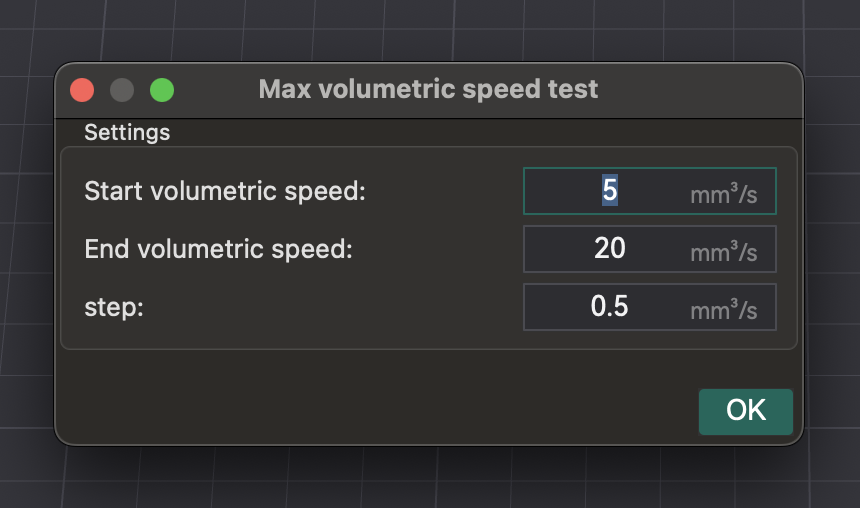
- Teste: o OrcaSlicer gera um modelo. Imprima-o e observe a qualidade conforme a velocidade (e o fluxo volumétrico) aumenta. Identifique onde a qualidade de impressão se degrada (subextrusão, lacunas, superfície rugosa).
- Identificando a Velocidade Máxima Segura: Anote a velocidade volumétrica imediatamente antes da degradação. Esta é a sua velocidade volumétrica máxima segura para aquele hotend e filamento.
- Aplicando Configurações: Insira este valor nas configurações do filamento no OrcaSlicer. Isso evita que o fatiador comande velocidades que excedam a capacidade do seu hotend.
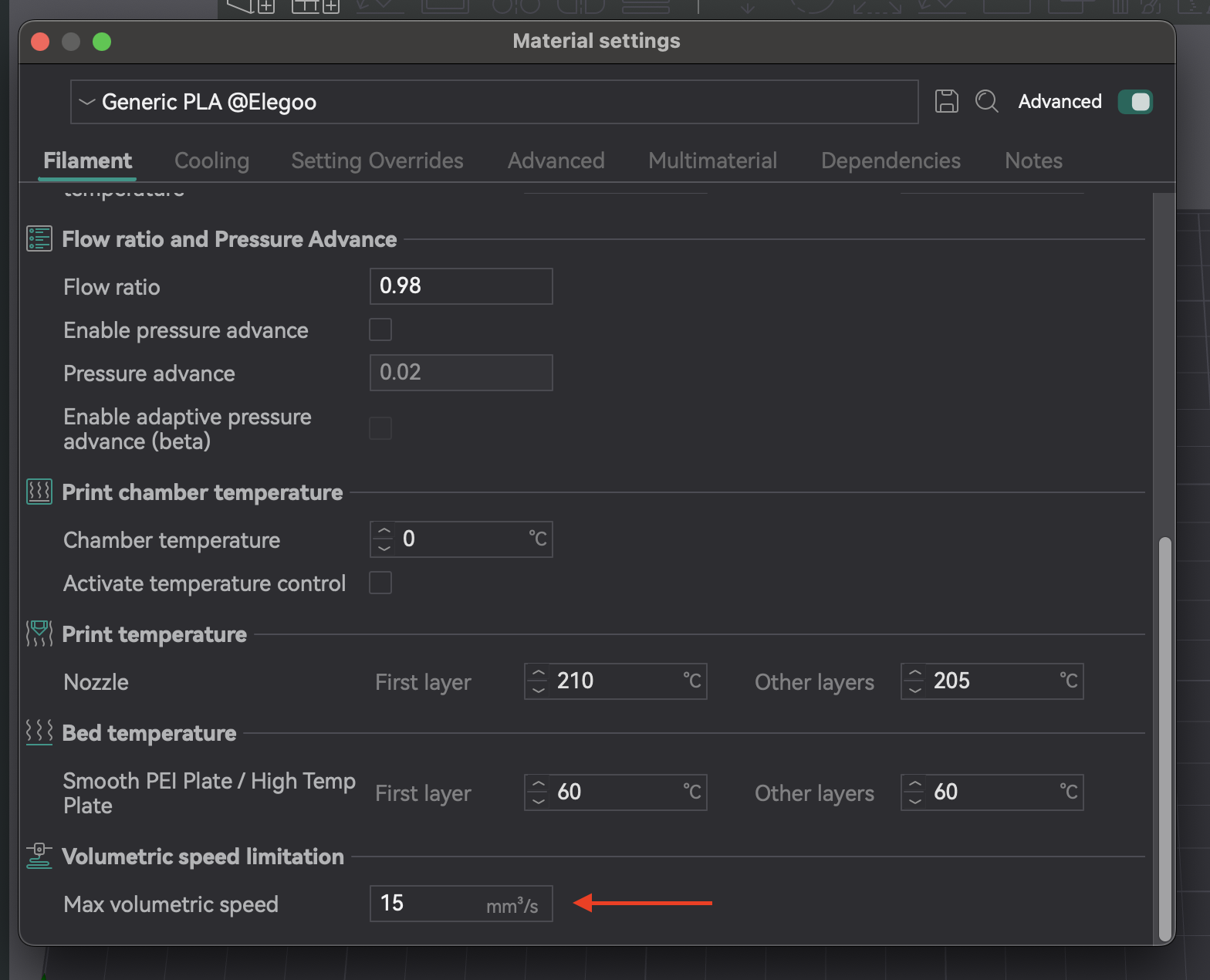
| Tipo/Marca de Filamento | Velocidade Volumétrica Máxima Ótima (mm³/s) | Observações |
|---|---|---|
| PLA (Genérico) | 16,75 | Subextrusão e lacunas entre camadas além deste ponto |
| PETG (Prusament) | 14,5 | Degradação da qualidade da superfície em velocidades mais altas |
| ABS (Hatchbox) | 18,0 | Extrusão consistente até este limite |
Tabela 6: Resultados da Velocidade Volumétrica Máxima
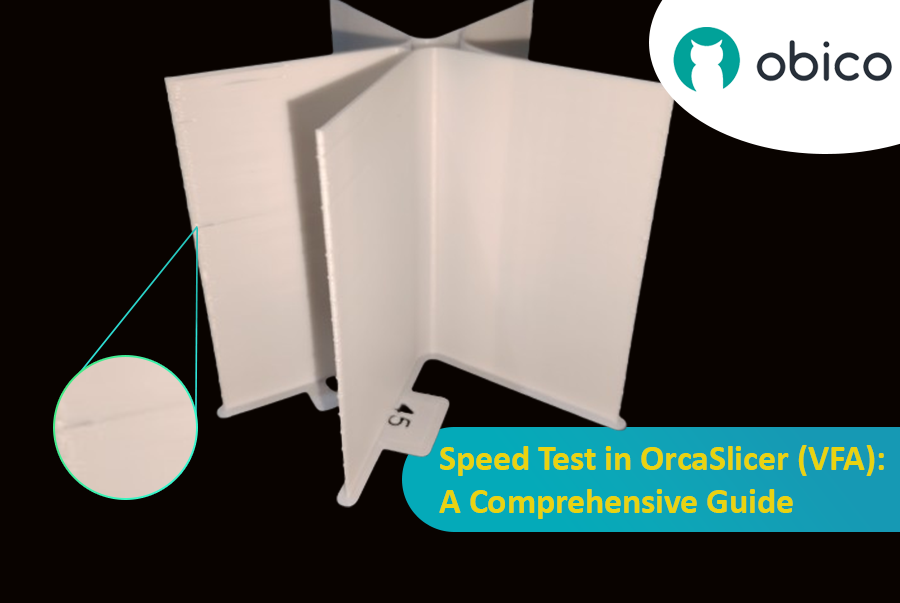
7. Calibração VFA (Vertical Fine Artifacts): Suavizando suas impressões
Artefatos Finos Verticais (AFVs) são padrões ou linhas sutis e rítmicas em impressões, geralmente próximos a cantos ou mudanças de direção. São causados por vibrações mecânicas ou ressonância no sistema de movimento em alta velocidade.
A calibração VFA encontra o limite prático de velocidade para qualidade, diferente da Velocidade Volumétrica Máxima. Enquanto a velocidade volumétrica se refere à capacidade do hotend, a VFA aborda as limitações do sistema de movimento. Sua impressora pode extrudar filamento suficiente, mas sua estrutura, correias ou motores podem introduzir vibrações como VFAs. O teste VFA fornece uma velocidade máxima de impressão "real" onde a qualidade é mantida, verificando a estabilidade do sistema de movimento após a velocidade volumétrica ser definida.
Usando o teste de velocidade VFA no OrcaSlicer
- Acesso: Vá em "Calibração" > "Mais" > "VFA".
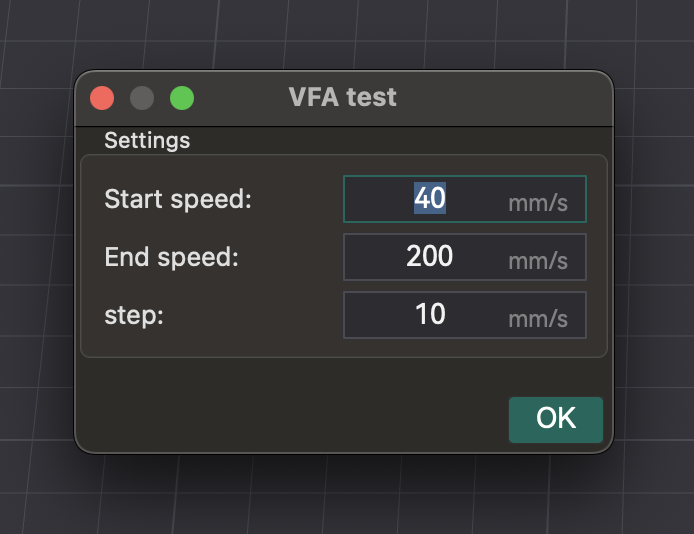
- Configuração de Parâmetros: Uma janela aparece para configurar "Velocidade inicial", "Velocidade final" e "Incrementos de passo". Exemplo: início de 160 mm/s, final de 500 mm/s, incrementos de 20 mm/s.
- Análise de Defeitos: Fatie e imprima a torre de velocidade VFA. Inspecione visualmente quanto a encadeamentos, subextrusão, deslocamentos de camada e acabamento superficial. Identifique a velocidade mais alta com boa qualidade antes da degradação. O modelo possui marcações correspondentes às velocidades. Exemplo: se a subextrusão começa no entalhe 11 (início de 160 mm/s, incrementos de 20 mm/s), a velocidade ideal �é 360 mm/s (160 + (20 * 10)).
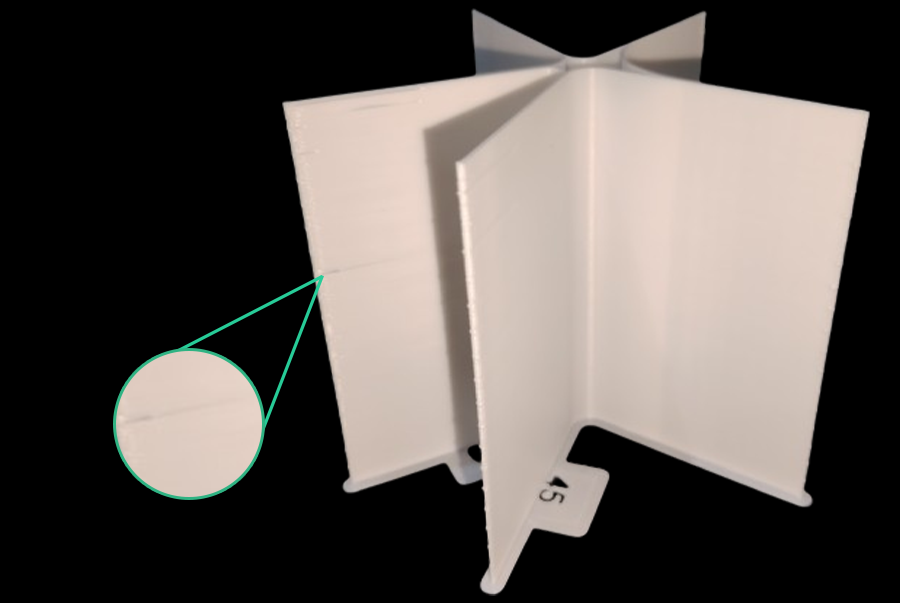
Fonte: obico.io
Dicas avançadas e solução de problemas
A qualidade ideal da impressão 3D exige mais do que apenas testes de calibração. É preciso manutenção da impressora, gerenciamento de filamentos e controle ambiental.
Mantendo uma impressora limpa e calibrada
A manutenção regular é fundamental: verifique se há desgaste/entupimentos no bico, garanta o funcionamento da extrusora, limpe a mesa e verifique a tensão da correia. A limpeza de rotina, o nivelamento da mesa e o ajuste do PID mantêm sua impressora otimizada.
Usando filamento fresco e seco
A qualidade do filamento afeta as impressões. A umidade em filamentos higroscópicos (PETG, Nylon, TPU) causa bolhas, chiados, formação de fios e peças frágeis. Use sempre filamento novo e seco. Armazene em sacos/recipientes lacrados com dessecante. Seque o filamento úmido em uma secadora ou forno.
A importância de um ambiente de impressão consistente
Um ambiente estável é crucial. Flutuações de temperatura, umidade ou fluxo de ar causam deformações e inconsistências. Use um gabinete, se possível. Monitore com um termômetro e um higrômetro para evitar problemas.
Quando recalibrar
A calibração é contínua, não é algo do tipo "configure e esqueça". As configurações são dinâmicas e mudam.
- Novo filamento: Recalibre para novos tipos, marcas ou até mesmo cores.
- Alterações de hardware: Novos hotends, extrusoras ou alterações no comprimento do tubo Bowden exigem a recalibração dos parâmetros afetados.
- Degradação da qualidade de impressão: Se a qualidade cair inesperadamente, a recalibração costuma ser o primeiro passo para diagnosticar a causa.
Fluxograma geral de solução de problemas para problemas de qualidade de impressão
Muitos problemas de qualidade de impressão decorrem de problemas de calibração. Utilize uma abordagem sistemática para diagnosticá-los e resolvê-los, evitando ajustes aleatórios. Problemas durante a calibração do fluxo (cliques, impressões irregulares) geralmente indicam problemas de pré-calibração ou dependências como temperatura ou passos E. Comece com verificações básicas antes de calibrações específicas do fatiador.
| Problema | Possível causa da calibração | Primeiros passos para verificar |
|---|---|---|
| Má adesão da primeira camada | Deslocamento Z, nivelamento da cama, temperatura | Renivele a cama (manual/automático), ajuste o deslocamento Z, verifique a temperatura da cama. |
| Fio de filamento/exsudação | Retração, temperatura, vazão | Filamento seco, repita o teste de retração, verifique a temperatura do bico. |
| Cantos arredondados/borbulhados | Avanço de pressão, velocidade de impressão | Repita o teste de PA (considere o método da torre), reduza a velocidade de impressão. |
| Subextrusão/Lacunas | Vazão, temperatura, velocidade volumétrica máxima | Repita a calibração de vazão, aumente a temperatura do bico, verifique se há obstruções. |
| Superextrusão/Superfícies ásperas | Vazão, temperatura | Repita a calibração de vazão, diminua a temperatura do bico. |
| Imprecisão Dimensional | Tolerância, Vazão | Repetir o teste de tolerância, verificar a compensação X-Y. |
| Artefatos Finos Verticais (AFVs) | Calibração de AFV, Modelagem de Entrada, Problemas Mecânicos | Repetir o teste de AFV, verificar correias/estrutura, considerar Modelagem de Entrada. |
| Mudanças de Camada | Problemas Mecânicos (correias, motores), Aceleração | Verificar a tensão das correias, inspecionar a estrutura, reduzir a aceleração. |
Tabela 7: Fluxograma de solução de problemas de qualidade de impressão (conceitual)
Conclusão
A calibração completa com o OrcaSlicer é uma prática indispensável para qualquer entusiasta ou profissional de impressão 3D. Ao ajustar cuidadosamente parâmetros como temperatura, vazão, avanço de pressão, retração, tolerância, velocidade volumétrica máxima e VFA, você libera todo o potencial da sua impressora. Essa precisão resulta em impressões de maior qualidade, confiabilidade e precisão, reduzindo o desperdício de filamentos e aumentando as taxas de sucesso.
A calibração é um processo contínuo. À medida que você introduz novos filamentos, modifica hardware ou vivencia mudanças ambientais, reavalie e ajuste suas configurações. Essa otimização contínua garante que sua impressora tenha um desempenho consistente e máximo. Boa impressão!
Also available in: Deutsch | English | Español | Français | Italiano | Nederlands | Polski | Русский
In the 3D printing world, the initial setup of your print is just as important as the model you’re trying to bring to life. One of the most critical and often overlooked components of this setup is the Start G-code, a set of instructions that prepares your 3D printer for the actual print. Whether you use Orca Slicer, a feature-rich slicing software that is based on Bambu Studio and PrusaSlicer, or another slicer, understanding and customizing the Start G-code can be the key to better prints and a smoother workflow.
In this article, we will go deep into what is Start G-code, why it’s important for perfect prints, how to edit it in Orca Slicer, and how to customize it for any 3D printer. We will also explain the Start G-code in the well-known Elegoo Neptune 4 Pro in Orca Slicer as an example for better understanding.
By the end of this article, you will know how Start G-code works, how to tweak it for best results, and how to use advanced techniques like Klipper macros to make your G-code simpler more readable and easier to update.
Ever seen those little strings hanging off your 3D print like tiny spider webs? Or the nozzle scratching over a beautiful layer? If you’ve experienced these issues, you’re not alone—and there’s a fix. Enter Z-Hop, a feature in Orca Slicer that will take your 3D prints from good to great.

Whether you’re new to 3D printing or a hobbyist, getting the settings right makes a huge difference. In this guide, we’ll be exploring Z-Hop—what it is, how to use it, and why it’s a game changer.
Let’s get started!
Introdução
No mundo da impressão 3D, o software de fatiamento que você escolher pode impactar significativamente a qualidade, a velocidade e a eficiência das suas impressões. Dois fatiadores populares que estão fazendo sucesso na comunidade são o Orca Slicer e o Bambu Studio. Ambos oferecem um conjunto robusto de recursos adaptados a diferentes usuários, mas qual é o ideal para você?

Neste guia, compararemos os dois segmentadores, abordando instalação, interface do usuário, recursos de destaque, suporte da comunidade e muito mais.
Não importa se você é iniciante ou experiente em impressão 3D, isso ajudará você a escolher o fatiador certo para suas necessidades.
Introduction
3D printing is a great technology that turns designs into real objects, but figuring out the best print speed can be tricky. If you go too fast, quality may be lost; if you go too slow, it takes forever.
In this guide, we will show you how to use OrcaSlicer to determine the perfect print speed for your 3D printer. By the end of it, you will know how to get great prints quickly while maintaining good quality.
Let’s get started!
Hello there! Welcome to our easy-to-understand guide on how to control the OrcaSlicer maximum volumetric speed test for 3D printing enthusiasts. If you’re looking forward to enhancing print quality and efficiency, then this is the best place for you. This tutorial will help you optimize your printer’s volumetric speed that determines at what speed you can print without compromising on quality.
Volumetric speed knowledge is crucial in 3D printing because it enables one understand how fast a printer can produce objects with accuracy. If this speed is tested and adjusted, under extrusion among other common problems while printing can be avoided thus ensuring that all your prints are good-looking even at higher speeds.
Introduction
3D printing has revolutionized the way creators, engineers, and hobbyists bring their ideas to life. However, the transition from a digital model to a tangible object isn’t always straightforward. One key challenge is ensuring parts fit together seamlessly. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of tolerance testing using OrcaSlicer, a valuable tool for 3D printing. We will understand together how to know the right tolerances value to design successful prints which fit together well.
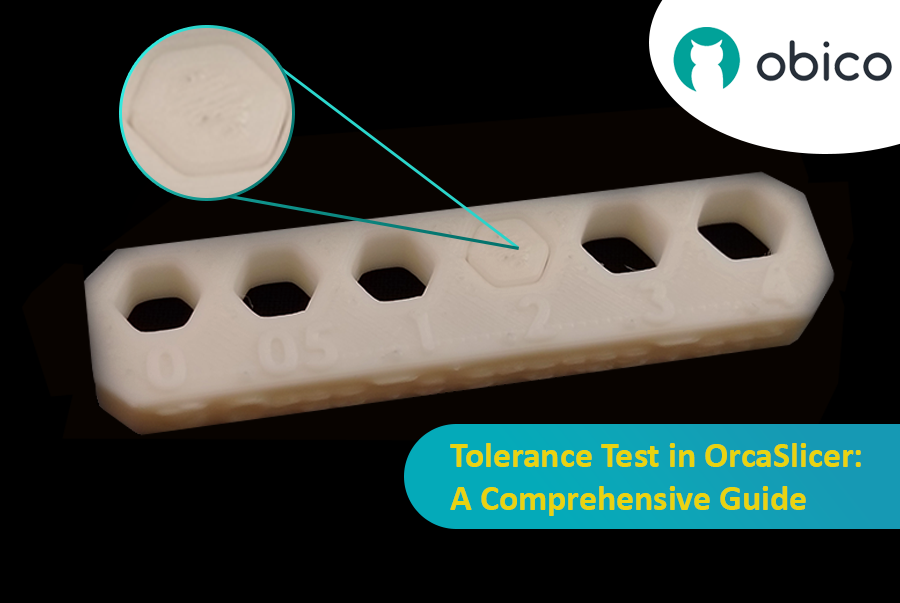

But before we get started testing our 3D printer, let’s understand some important related topics.
The Importance of Tolerance in 3D Printing
In the world of 3D printing, tolerance is all about precision. It's the measure of how accurately a 3D printer can replicate the dimensions specified in your digital design. Imagine you're creating a puzzle; if the pieces are too big or too small, they won't fit together. Similarly, for 3D printed parts to function and fit together as intended, the printer must be able to accurately produce parts within very tight dimensional limits. Good tolerance affects everything from how smoothly moving parts interact to the overall look and strength of the finished product.
But why do you need to make the tolerance test?
Well, in 3D printing things do not always go right. Every filament type has its own shrinkage coefficient and this affects how your print turns out. Different printers, with their unique mechanics and settings, can also produce varied results. That's why testing for tolerance is crucial - it helps you understand how your specific printer and chosen filament behave together, allowing you to adjust the tolerances in your design for the perfect print.
Try JusPrin, the first GenAI 3D printing tool built on OrcaSlicer.
Visão geral do avanço de pressão
Imagine que você está desenhando com uma caneta que às vezes derrama muita tinta e outras vezes quase nada. Na impressão 3D, algo semelhante pode acontecer quando a impressora se move rapidamente e muda de velocidade – isso pode afetar a quantidade de plástico que sai.
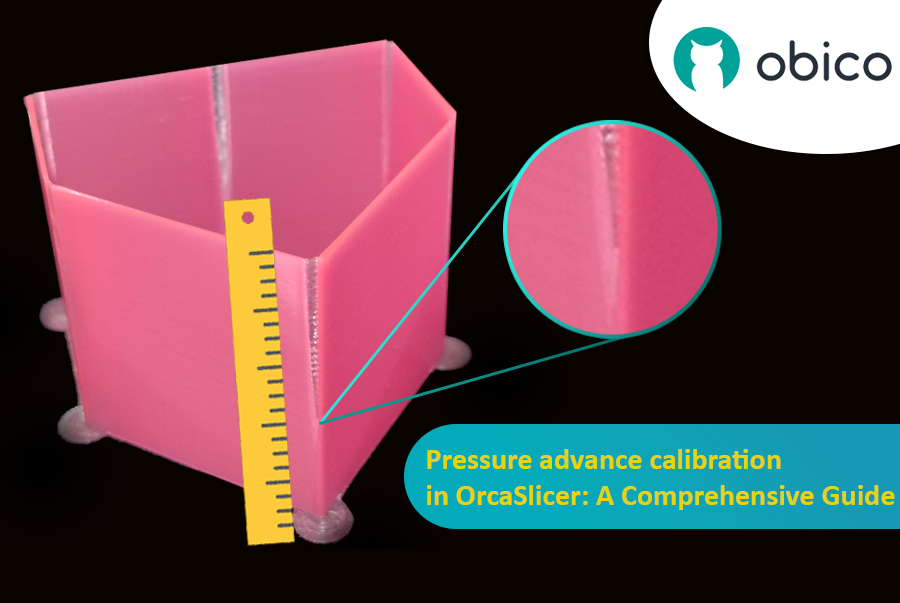
Mas por que sua impressora às vezes erra na quantidade de plástico que sai?
Em uma impressora 3D, o filamento sai com base na pressão exercida dentro do bico. É como uma mangueira de jardim: você precisa de pressão de água suficiente antes que ela esguiche. Quando a impressora acelera ou desacelera, como ao fazer curvas, demora um pouco para que a pressão do bico se ajuste. Se a impressora se mover muito rápido e muito cedo, não sai filamento suficiente. E se ela desacelerar muito rápido, sai filamento demais. Isso pode fazer com que os cantos da sua impressão pareçam um pouco bagunçados, porque a impressora não ajustou o fluxo do filamento corretamente para as mudanças de velocidade.
E �é aqui que o Avanço de Pressão entra em ação. É um recurso inteligente que compensa essas mudanças, garantindo que a quantidade certa de filamento seja extrudada conforme a impressora acelera ou desacelera. Com o Avanço de Pressão, sua impressora lida melhor com as transições de velocidade, resultando em impressões mais suaves e nítidas, especialmente nos cantos mais difíceis.
Introduction
3D printing is a fascinating technology that allows you to create almost anything you can imagine. However, it also comes with some challenges and limitations, such as the quality of the printed parts. One of the most common issues that affect the appearance and functionality of 3D prints is the presence of unwanted material residues, such as strings, blobs, and zits.
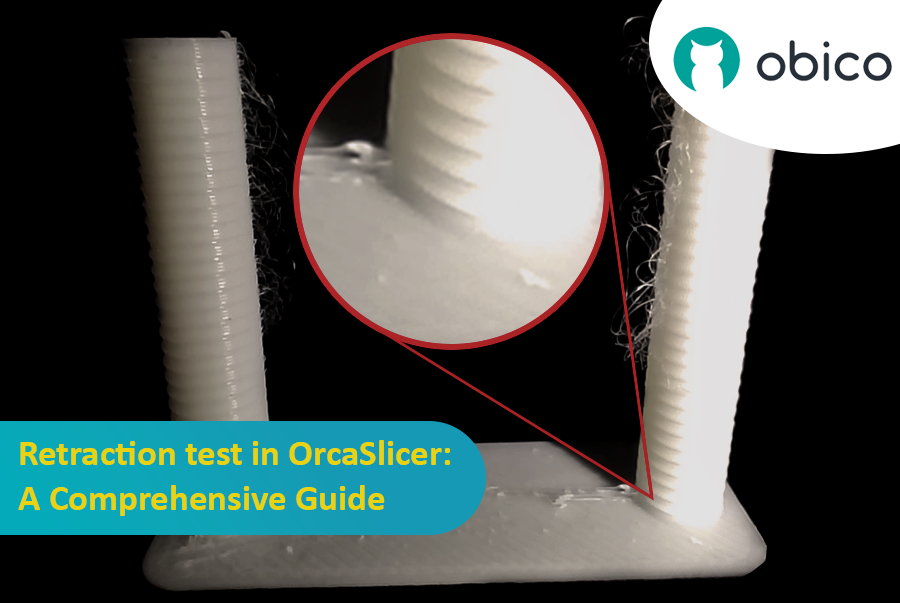
Fortunately, there is a way to reduce or eliminate these artifacts by using a feature called retraction. But what does retraction mean?
Let’s break it down:
What is the retraction and the retraction test?
The retraction test is a calibration procedure that aims to reduce or eliminate the stringing and oozing problems that may occur during 3D printing. Stringing and oozing are caused by the excess material that leaks out of the nozzle when the hotend moves from one part of the model to another without extruding. This results in unwanted strands or blobs of filament on the surface or between the parts of the model, affecting the quality and appearance of the print.
